18.05.2020
Preparations are underway for Arianespace’s upcoming Vega and Ariane 5 missions

A pair of important arrivals this week – one by air, the other by sea – marked an acceleration of preparations at Europe’s Spaceport for Arianespace’s next two missions, to be performed from French Guiana with its lightweight Vega and heavy-lift Ariane 5 launch vehicles.
These parallel arrivals involved personnel who will conduct the first Vega “rideshare” mission, scheduled for mid-June to orbit 53 small satellite payloads; and Ariane 5 launch vehicle components for a three-passenger flight planned for liftoff this summer.
Team members for the Vega launch campaign were flown in aboard a chartered airliner that touched down at Félix Eboué Airport near the French Guiana capital city of Cayenne. They will be responsible for preparing this mission’s liftoff from the Vega Launch Complex (ZLV), located on the Kourou side of the Spaceport.
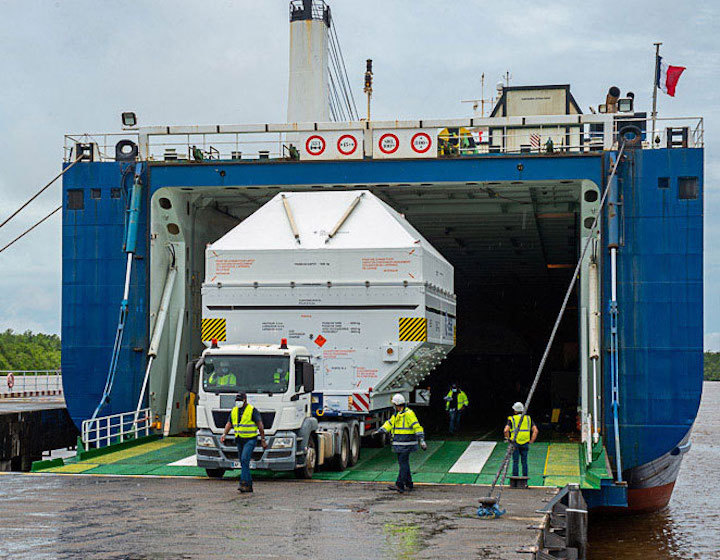

As the personnel were settling in, main launcher components for the Ariane 5 flight were being unloaded from the MN Toucan, one of two roll-on/roll-off sea-going ships operated for Arianespace, which docked at Paricabo Port near Kourou. After unloading, the components were to be taken by road to the Ariane 5’s ELA-3 launch complex – also situated on the Spaceport’s Kourou side.
Launch activities in French Guiana had been suspended mid-March because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and were gradually resumed – carried out in strict compliance with health rules published by the Prefect of French Guiana, as well as the French CNES space agency and the Guiana Space Center.
Vega proof-of-concept flight for SSMS
Designated Flight VV16 in Arianespace’s numbering system, Vega’s mission will be the first of the Small Spacecraft Mission Service (SSMS) – a program initiated by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2016, with the contribution of the European Commission. For all the European partners involved, its purpose is to perfectly address the burgeoning microsatellite market for institutional and commercial customers alike.
The modular SSMS dispenser was designed to be as market-responsive as possible, able to accommodate a wide combination of payloads – from a main large satellite with smaller companions to multiple smaller satellites, or dozens of individual CubeSats.
Flight VV16 will be Arianespace’s fifth launch overall in 2020, and its first this year using the lightweight Vega member of its launch vehicle family – which also includes the heavy-lift Ariane 5 and medium-lift Soyuz.
The satellite passengers on Flight VV16 will be deployed by Vega to Sun-synchronous orbits. They will serve different types of applications, such as Earth observation, telecommunications, science and technology/education.
Readying Ariane 5’s three-satellite payload
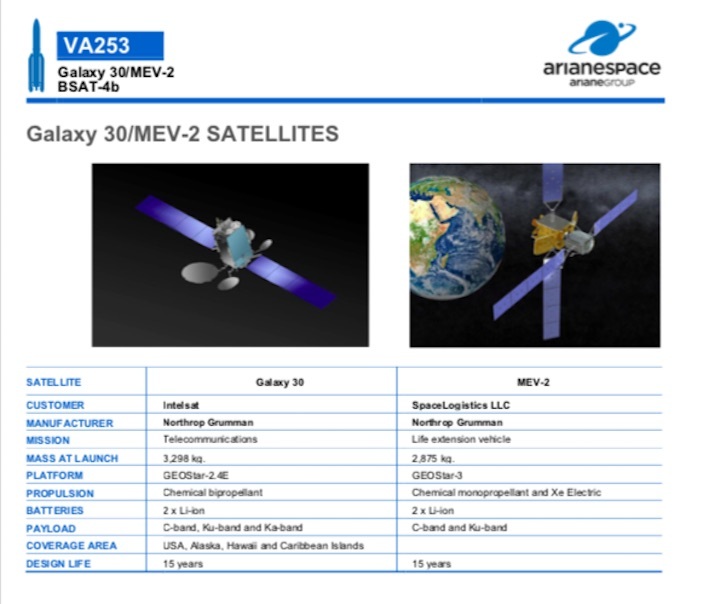
For Arianespace’s initial Ariane 5 mission following the resumption of operational activity at the Spaceport, its heavy-lift launcher will carry three payloads to geostationary transfer orbit: the Galaxy 30 and BSAT-4b telecommunications satellites, along with a Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV).
Riding in Ariane 5’s upper payload position will be Galaxy 30, produced by Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems (NGIS). This is the first spacecraft built under Intelsat’s North American satellite fleet replacement program and highlights the operator’s continued focus on C-band communication technologies.
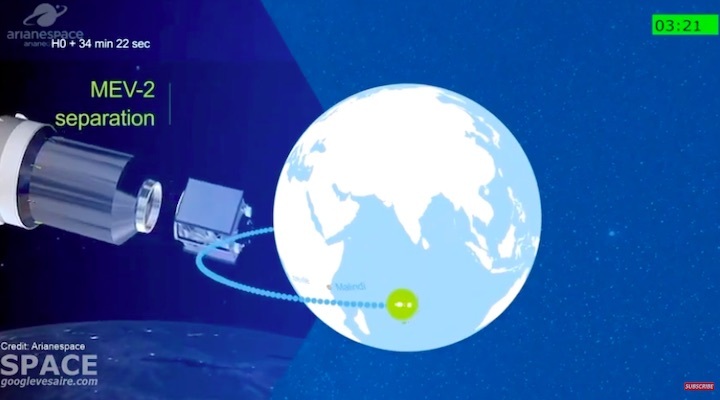
To be deployed as a Galaxy 30 “piggyback” payload is Northrop Grumman’s second Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV-2) – a servicing spacecraft that docks with an existing satellite in orbit to provide life-prolonging propulsion and attitude control. After deployment by Ariane 5, MEV-2 will service the Intelsat 10-02 satellite, which was launched in 2004.
Flight VA253’s other passenger on Ariane 5 – BSAT-4b – was built by Maxar Technologies for Japan’s Broadcasting Satellite System Corporation (B-SAT) as a back-up to BSAT-4a, launched by Arianespace in 2017. BSAT-4b uses Maxar Technologies’ 1300 Class platform and carries Ku-band transponders.
Quelle: arianespace
----
Update: 24.07.2020
.
Arianespace to launch three satellites towards Geostationary Orbit on July 28

Final step in Ariane 5 latest performance improvement program decided in 2016, Flight VA253 brings the total increase in payload capacity to 300 kg since then.
The two of the three companies whose satellites are being launched are both long-standing customers – Intelsat for 37 years and B-SAT for 23 years – clearly proving the excellence of Arianespace’s service offering and long-term customer relations.
The third, Northrop Grumman’s wholly-owned subsidiary, SpaceLogistics LLC, is a first-time customer to Arianespace.
Since the reopening of the Guiana Space Center in French Guiana, teams from Arianespace and ArianeGroup have focused on preparing this very innovative mission under the best possible conditions.
Arianespace’s next Ariane 5 launch from the Guiana Space Center (CSG) in Kourou, French Guiana, is scheduled for Tuesday, July 28, in a launch window from 21:29 UTC to 22:15 UTC.
Satellites to be placed in orbit will serve Japanese B-SAT and operators Intelsat and Northrop Grumman’s SpaceLogistics LLC. BSAT-4b was built by the American company Maxar Technologies and will be used to broadcast Ultra-High-Definition (UHD, 4K and 8K) direct-to-home television broadcasting across Japan, in conjunction with its twin, BSAT-4a, also built by Maxar and launched by Arianespace in 2017.
The other two satellites on this mission were built by the American company Northrop Grumman: the Galaxy 30 UHD video distribution/broadcast and broadband satellite, built for the global network operator, Intelsat, will cover North America, and MEV-2 (Mission Extension Vehicle), a highly innovative satellite servicing vehicle designed to dock to satellites in orbit to provide life extension services. The first customer for MEV-2 will be the Intelsat 10-02 satellite, in geostationary orbit since 2004. MEV-2 will provide five years of service to this satellite.
This mission will use the Ariane 5 heavy-lift launcher, developed and manufactured by ArianeGroup, which has increased its payload capacity by 85 kg for this flight, thanks to the introduction of a new vehicle equipment bay (VEB), bringing total payload capacity into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) to 10,200 kg. Since kicking off a continuous improvement program for Ariane 5 in 2016, ArianeGroup has increased this launcher’s payload capacity by 300 kg for the benefit of Arianespace. Their customers will continue to benefit from this enhanced performance on Ariane 5 for the rest of its missions.
The Ariane 5 launcher is a joint European government-industry program. Arianespace is responsible for marketing and operating Ariane 5 launches from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana, with support from the French space agency CNES and the European Space Agency (ESA). ArianeGroup is in charge of all design and production, from initial design studies, upgrades and manufacturing, to the supply of data and software for each mission. Its specific responsibilities include the production of equipment, structures and propulsion systems, integration of the different stages, and integration of the complete launcher in French Guiana.

Quelle: arianespace
----
Update: 26.07.2020
.
The next Ariane 5 launch is postponed
To enable additional technical checks required under the fairing and the Ariane dual launch system (SYLDA), the final phase of launch preparation operations for the 253rd Ariane flight (VA253) has not been initiated by Arianespace.
The soonest possible launch date for this mission is Friday, July 31 at:
- 5:30 p.m., Washington, D.C. time,
- 6:30 p.m., Kourou, French Guiana time,
- 9:30 p.m., Universal Time (UTC),
- 11:30 p.m., Paris time.
The Ariane 5 launch vehicle and its three spacecraft payloads are in stable and safe condition.
Quelle: arianespace
----
Update: 1.08.2020
.
Delay of Flight VA253 with Ariane 5
Flight VA253 has been postponed due to a “red” during the final countdown. The “red” was related to a sensor on the Ariane 5 cryogenic main stage’s liquid hydrogen fuel tank.
The Ariane 5 launch vehicle and its three spacecraft payloads are in stable and safe condition.
The soonest possible launch date is Saturday, August 1 at:
- 5:30 p.m., Washington, D.C. time,
- 6:30 p.m., Kourou, French Guiana time,
- 9:30 p.m., Universal Time (UTC),
- 11:30 p.m., Paris time.
Quelle: arianespace
+++
----
Update: 13.08.2020
.
Ariane 5 is given the go-ahead for launch on August 14 with a triple satellite payload

Arianespace Flight VA253 – which will utilize an increased-lift Ariane 5 version – is a “go” for launch on August 14 following an additional Launch Readiness Review (LRR) performed today in French Guiana.
This approval clears the way for Ariane 5’s return to the Spaceport’s ELA-3 launch zone tomorrow, followed by the final countdown leading to an evening liftoff on Friday.
The mission to geostationary transfer orbit will deploy two telecommunications satellites: Galaxy 30 for Intelsat, and BSAT-4b for B-SAT, both of which are long-time Arianespace customers. Also carried by Ariane 5 is the Mission Extension Vehicle-2 (MEV-2) for Northrop Grumman’s wholly-owned subsidiary, SpaceLogistics LLC, which is a first-time user of Arianespace launch services.
Galaxy 30 was built by Northrop Grumman for Intelsat and will be the first payload deployed during the Ariane 5 mission. This satellite is to provide Ultra-High-Definition video distribution/broadcast and broadband services that cover North America.
MEV-2 is stacked under Galaxy 30 on Ariane 5, and is to be the second payload released during Flight VA253. The SpaceLogistics LLC-built spacecraft is designed to offer life extension services for in-orbit satellites, and its initial target is the Intelsat 10-02 relay platform, which has been in geostationary orbit since 2004.
Completing Flight VA253’s mission sequence will be the deployment of BSAT-4b, configured for Ultra-High-Definition (UHD, 4K and 8K) direct-to-home television broadcasting across Japan. Built by Maxar Technologies, BSAT-4b will be operated by Japan’s Broadcasting Satellite System Corporation (B-SAT).
The launcher configuration used for Flight VA253 marks the final step in Ariane 5’s latest performance improvement program, which was decided in 2016 and has increased the launch vehicle’s total payload capacity by 300 kg. ArianeGroup is production prime contractor for Ariane 5, delivering the launcher to Arianespace for operation.
Liftoff of Flight VA253 is planned as early as possible within the following launch window on August 14:
- Between 5:33 p.m. and 6:20 p.m. Washington, D.C. time,
- Between 6:33 p.m. and 7:20 p.m. Kourou, French Guiana time,
- Between 21:33 and 22:20 Universal time (UTC),
- Between 11:33 p.m. and 12:20 a.m. Paris time, in the night of August 14 to August 15,
- Between 06:33 a.m. and 07:20 a.m. Japan time, in the morning of August 15.
Quelle: arianespace
----
Update: 15.08.2020
.
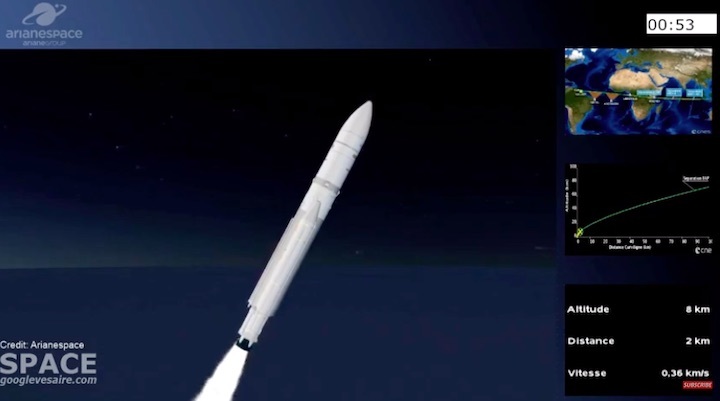
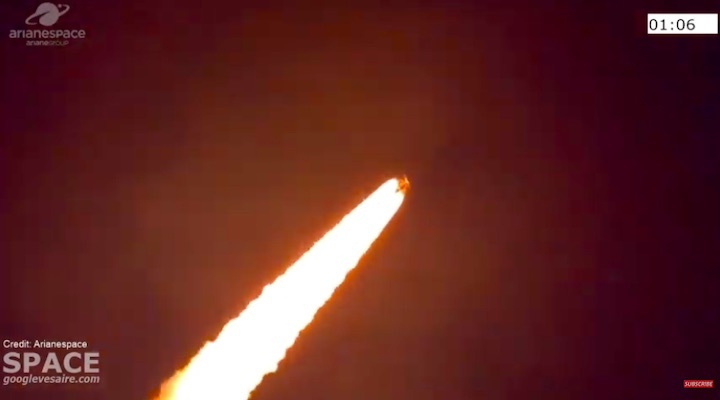
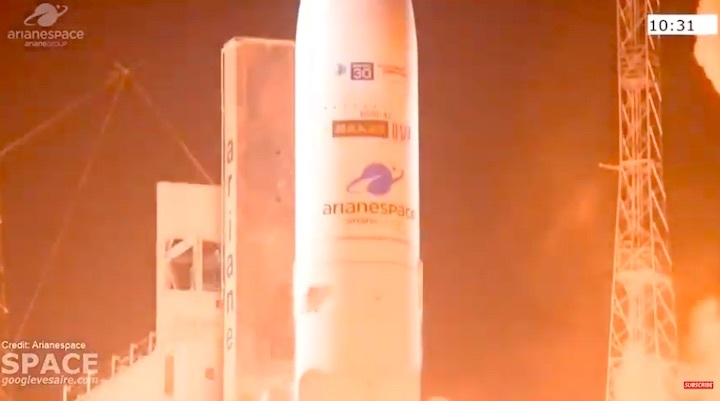















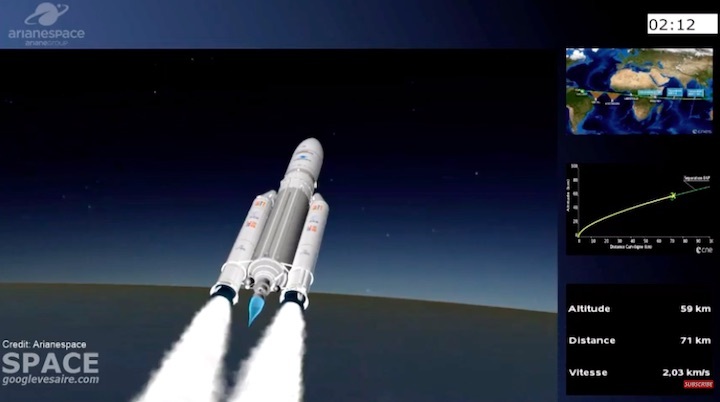

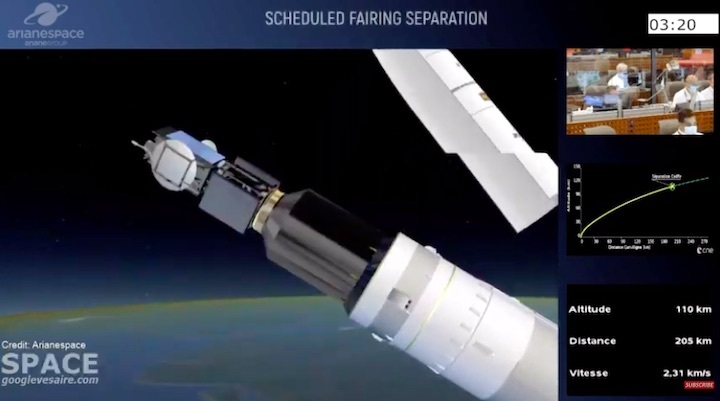

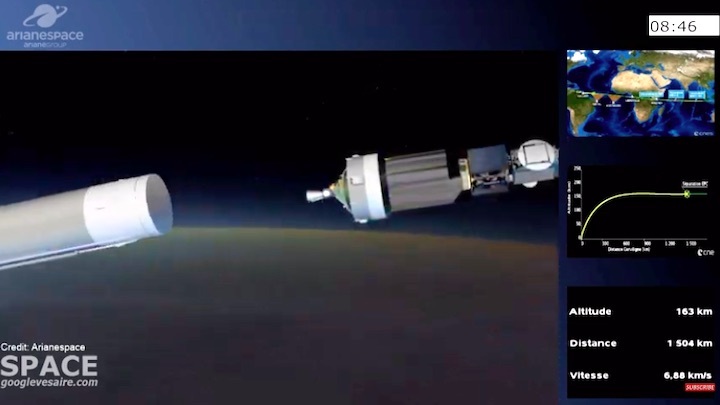



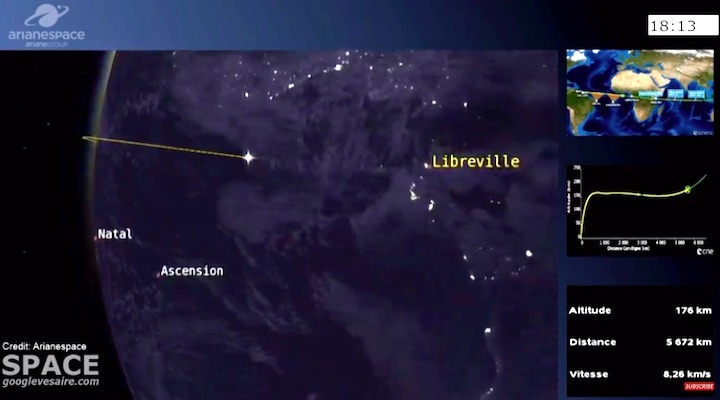

Quelle: arianespace
+++
Arianespace’s Ariane 5 orbits Galaxy 30, MEV-2 and BSAT-4b

The Ariane 5 for Arianespace’s Flight VA253 was equipped with a new vehicle equipment bay that enabled the launcher’s payload capacity to be increased.
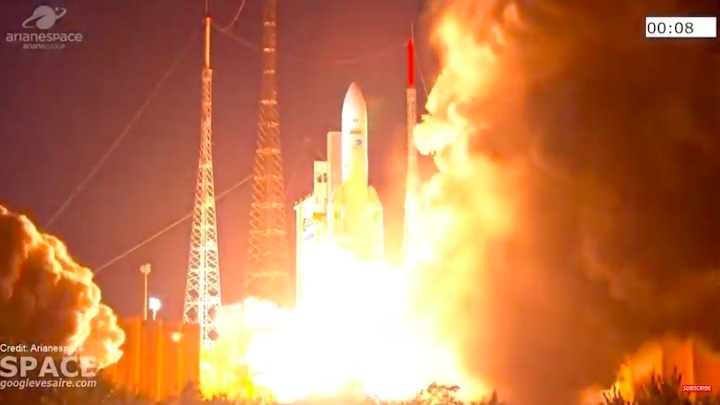
Ariane 5 flexed its heavy-lift muscles on Arianespace’s latest launch from the Spaceport in French Guiana, successfully placing the triple payload of Galaxy 30 (G-30), the Mission Extension Vehicle-2 (MEV-2) and BSAT-4b into geostationary transfer orbit.
Designated Flight VA253 in Arianespace’s numbering system, today’s mission was performed from the Spaceport’s ELA-3 launch zone – with Ariane 5 deploying its three passengers during a sequence lasting 47 minutes from liftoff to final separation. It marked the 253rd launch of an Ariane-series vehicle to date, and the 109th using an Ariane 5.
Today’s mission utilized an Ariane 5 ECA version with increased payload capacity through the introduction of a new vehicle equipment bay for the launch vehicle. Since kicking off a continuous improvement program for Ariane 5 in 2016, prime contractor ArianeGroup has increased the launcher’s payload capacity by 300 kg. for the benefit of Arianespace. This raises the total mass of payload passengers that can be carried by Ariane 5 to 10,200 kg.; for today’s mission, the combined mass of G30, MEV-2 and BSAT-4b was 9,703 kg.
“Flight VA253 marked another mission of innovation for us,” said Stéphane Israël, the Arianespace Chief Executive Officer. “This was the first time that we delivered three satellites to geostationary transfer orbit on a single launch, and it utilized the most capable Ariane 5 ever – with the increased payload capacity of 10.2 metric tons that is now available for satellite payloads.”
Continued success with Intelsat and Northrop Grumman
Deployed first in the flight sequence 27 minutes after liftoff, G-30 is the 62nd satellite Arianespace has launched for operator Intelsat, continuing a business relationship that extends back to 1983. It was produced by Northrop Grumman based on its GEOStar-2 platform, and will provide UHD video distribution/broadcast and broadband services that cover North America.
G-30 was carried as Ariane 5’s upper payload component, stacked with the MEV-2, built by Northrop Grumman’s wholly-owned company SpaceLogistics LLC. MEV-2 is designed to dock with geostationary satellites whose fuel has nearly depleted, thereby extending their useful lifetimes.
MEV-2 will rendezvous and dock in early 2021 with the Intelsat 10-02 (IS 10-02) satellite, originally launched in 2004. The Mission Extension Vehicle is to utilize its own thrusters and fuel supply to control the IS 10-02 satellite’s orbit.
Including G-30 and MEV-2, Arianespace has now orbited a total of 30 spacecraft produced by Northrop Grumman or its companies.
Another launch for Japan’s B-SAT with a Maxar-built satellite
The lower passenger in Ariane 5’s multi-payload configuration was BSAT-4b, which was orbited for the Japanese operator B-SAT. Produced by Maxar Technologies, it uses this manufacturer’s popular 1300-class spacecraft bus for commercial communications satellites.
BSAT-4b is designed for Ultra-High-Definition (UHD, 4K and 8K) direct-to-home television broadcasting across Japan in conjunction with its twin, BSAT-4a – which was launched by an Ariane 5 in 2017. All of BSAT’s 10 satellites have been orbited on Arianespace missions.
Ariane 5’s launch by the numbers
Flight VA253 was Arianespace’s fifth launch so far in 2020, and it follows two other heavy-lift Ariane 5 missions this year: the first orbited the EUTELSAT KONNECT and GSAT-30 satellites in January; while the second, performed in February, lofted JCSAT-17 and GEO-KOMPSAT-2B. Two medium-lift Soyuz missions also were conducted in February and March, with each successfully delivering 34 OneWeb constellation satellites to low Earth orbit.
The next mission in Arianespace’s 2020 manifest is the proof of concept flight for Europe’s Small Spacecraft Mission Service (SSMS) – which will deploy 46 small CubeSats and seven microsatellites from the light-lift Vega launcher, using a new-design rideshare dispenser system. This flight is planned for September 1.
Quelle: arianespace
