29.09.2019

NASA has given us another historic glimpse into the wonders of space after releasing a video that shows a star-shredding black hole in a galaxy millions of light-years away.
The amazing footage of the "cataclysmic phenomenon" was taken by NASA’s planet-hunting Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, or TESS.
Astronomers think the supermassive black hole weighs around 6 million times the sun’s mass and is located about 375 million light-years away in a galaxy of similar size to the Milky Way, NASA said.
The incredible event, called a tidal disruption, is very rare and occurs once every 10,000 to 100,000 years in galaxies like the Milky Way.
Hey, Ariana Grande! NASA interns had a blast remixing your song to promote moon mission
It came from outer space: Newly discovered comet is likely interstellar visitor
When a star gets too close, the intense tides of a black hole break apart the star into a stream of gas, according to NASA. As shown in the video, the tail of that stream breaks away from the black hole while other parts of it swing back around and create a halo of debris.
Scientists believe the star in the video may have been about the same size as our sun.
The event, named ASASSN-19bt, was first discovered on Jan. 29 by the All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae telescope network, a worldwide network of 24 robotic telescopes headquartered at Ohio State University.
NASA says that scientists have only been able to observe about 40 tidal disruptions in history and TESS was able to capture one after launching in April 2018.
“For TESS to observe (the event) so early in its tenure, and in the continuous viewing zone where we could watch it for so long, is really quite extraordinary,” said Padi Boyd, TESS project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
“Future collaborations with observatories around the world and in orbit will help us learn even more about the different outbursts that light up the cosmos.”
Quelle: USA TODAY
+++
This new visualization of a black hole illustrates how its gravity distorts our view, warping its surroundings as if seen in a carnival mirror. The visualization simulates the appearance of a black hole where infalling matter has collected into a thin, hot structure called an accretion disk. The black hole’s extreme gravity skews light emitted by different regions of the disk, producing the misshapen appearance.
Bright knots constantly form and dissipate in the disk as magnetic fields wind and twist through the churning gas. Nearest the black hole, the gas orbits at close to the speed of light, while the outer portions spin a bit more slowly. This difference stretches and shears the bright knots, producing light and dark lanes in the disk.
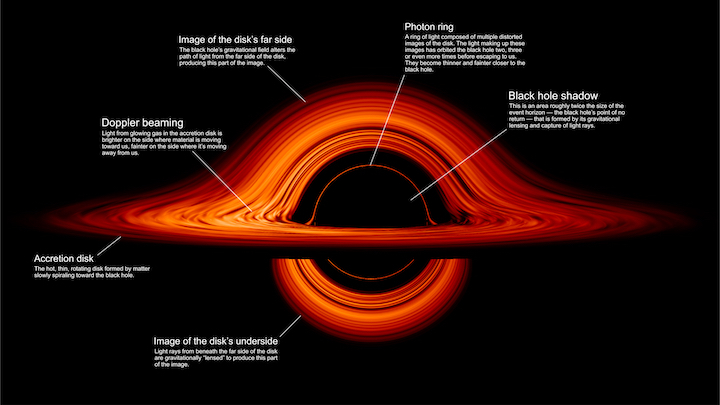
Viewed from the side, the disk looks brighter on the left than it does on the right. Glowing gas on the left side of the disk moves toward us so fast that the effects of Einstein’s relativity give it a boost in brightness; the opposite happens on the right side, where gas moving away us becomes slightly dimmer. This asymmetry disappears when we see the disk exactly face on because, from that perspective, none of the material is moving along our line of sight.
Closest to the black hole, the gravitational light-bending becomes so excessive that we can see the underside of the disk as a bright ring of light seemingly outlining the black hole. This so-called “photon ring” is composed of multiple rings, which grow progressively fainter and thinner, from light that has circled the black hole two, three, or even more times before escaping to reach our eyes. Because the black hole modeled in this visualization is spherical, the photon ring looks nearly circular and identical from any viewing angle. Inside the photon ring is the black hole’s shadow, an area roughly twice the size of the event horizon — its point of no return.
"Simulations and movies like these really help us visualize what Einstein meant when he said that gravity warps the fabric of space and time,” explains Jeremy Schnittman, who generated these gorgeous images using custom software at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “Until very recently, these visualizations were limited to our imagination and computer programs. I never thought that it would be possible to see a real black hole." Yet on April 10, the Event Horizon Telescope team released the first-ever image of a black hole’s shadow using radio observations of the heart of the galaxy M87.
Banner image: Seen nearly edgewise, the turbulent disk of gas churning around a black hole takes on a crazy double-humped appearance. The black hole’s extreme gravity alters the paths of light coming from different parts of the disk, producing the warped image. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Jeremy Schnittman
Quelle: NASA

