3.07.2025
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla.— Astronomers are monitoring an object headed our way that may have wandered over from another star system.
Scientists have discovered what might be only the third known interstellar object to pass through our solar system, the European Space Agency said Wednesday.
The harmless object is currently near Jupiter hundreds of millions of miles (kilometers) away and moving toward Mars, but it should get no closer to the sun than that, according to scientists.
It’s too soon to know whether the object, designated for now as A11pl3Z, is a rocky asteroid or a icy comet, or how big and what shape it is. More observations are needed to confirm its origins. NASA said it is monitoring the situation.
Astrophysicist Josep Trigo-Rodriguez of the Institute of Space Sciences near Barcelona, Spain, believes it is an interstellar object based on its odd path and extreme speed cutting through the solar system. He estimates its size at roughly 25 miles (40 kilometers) across.
The first confirmed interstellar visitor was in 2017. It was dubbed Oumuamua, Hawaiian for scout, in honor of the observatory in Hawaii that discovered it. Classified at first as an asteroid, the elongated Oumuamua has since showed signs of being a comet.
NASA Discovers Interstellar Comet Moving Through Solar System
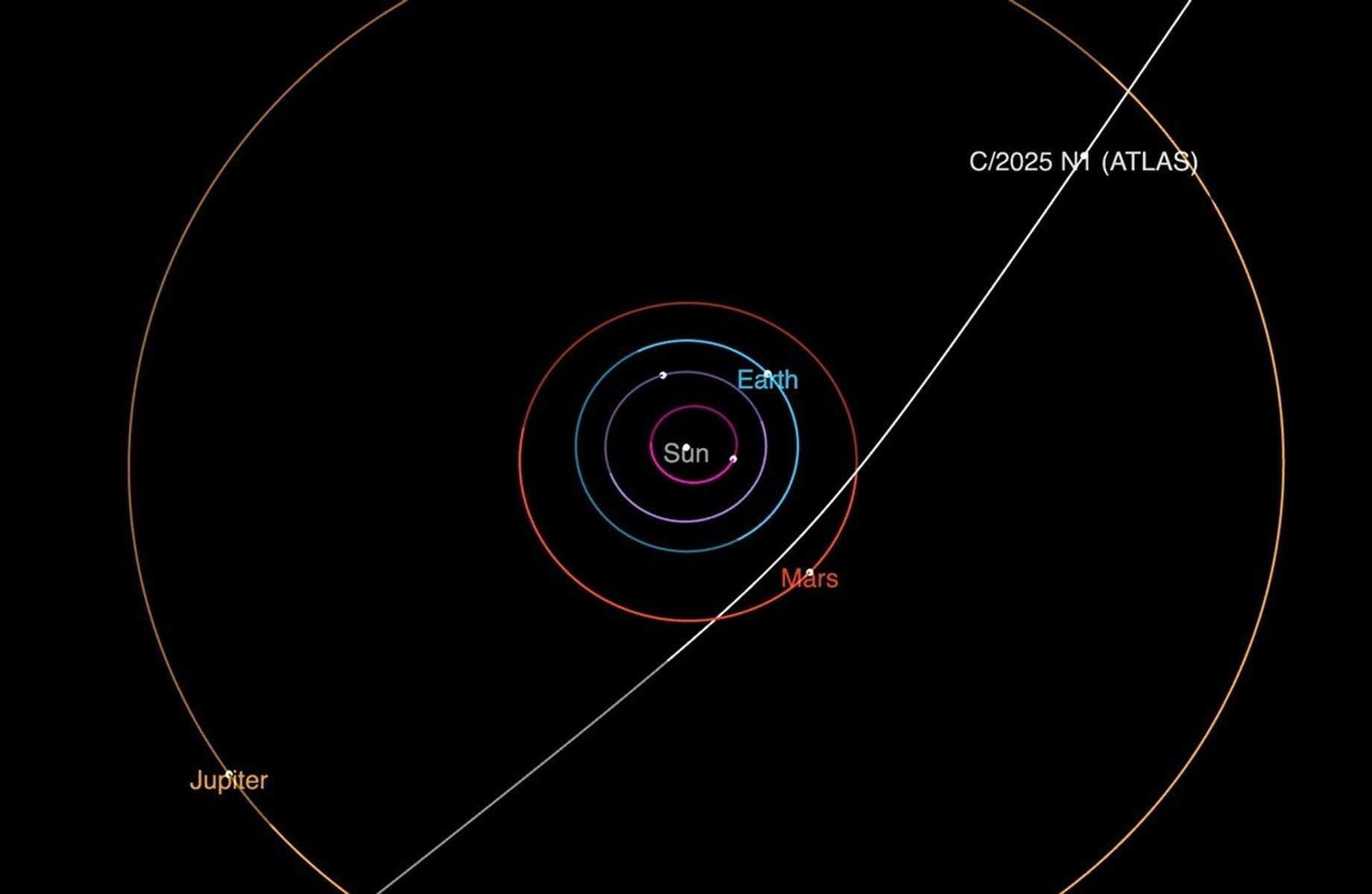
On July 1, the NASA-funded ATLAS (Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System) survey telescope in Rio Hurtado, Chile, first reported observations of a comet that originated from interstellar space. Arriving from the direction of the constellation Sagittarius, the interstellar comet has been officially named 3I/ATLAS. It is currently located about 420 million miles (670 million kilometers) away.
Since that first report, observations from before the discovery have been gathered from the archives of three different ATLAS telescopes around the world and the Zwicky Transient Facility at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California. These “pre-discovery” observations extend back to June 14. Numerous telescopes have reported additional observations since the object was first reported.
The comet poses no threat to Earth and will remain at a distance of at least 1.6 astronomical units (about 150 million miles or 240 million km). It is currently about 4.5 au (about 416 million miles or 670 million km) from the Sun. 3I/ATLAS will reach its closest approach to the Sun around Oct. 30, at a distance of 1.4 au (about 130 million miles or 210 million km) — just inside the orbit of Mars.
The interstellar comet’s size and physical properties are being investigated by astronomers around the world. 3I/ATLAS should remain visible to ground-based telescopes through September, after which it will pass too close to the Sun to observe. It is expected to reappear on the other side of the Sun by early December, allowing for renewed observations.
Quelle: NASA
----
Update: 5.07.2025
.
Astronomers spot 'interstellar object' speeding through solar system
This is the third time an object from outside the solar system has been found.
An "interstellar object" is speeding toward the inner solar system, where Earth is located, astronomers have confirmed.
The object -- likely a comet -- was first detected in data collected between by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System, or ATLAS -- an asteroid impact early warning system in Rio Hurtado, Chile, funded by NASA, the space agency announced on Tuesday.
Properties such as a marginal coma and short tail indicate signs of cometary activity, according to the Minor Planet Center.
Numerous telescopes have reported additional observations since the object was first reported, NASA said. Observations from three different ATLAS telescopes around the world -- as well as the Zwicky Transient Facility at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California -- dating back to June 14 were gathered and provided data that supports the existence of the comet, according to a NASA update released Wednesday.

It appears to be originating from interstellar space, arriving from the direction of the constellation Sagittarius, and is currently about 420 million miles from Earth, according to NASA.
The comet poses no threat to Earth and will remain at a distance of at least 150 million miles, astronomers said. It is estimated to reach its closest approach to the sun around Oct. 30, where it will cross at about 130 million miles away, just inside the orbit of Mars, according to NASA.
The object, dubbed "A11pl3Z" or "3I/ATLAS," spans approximately 25 miles, Josep Trigo-Rodriguez, as astrophysicist at the Institute of Space Sciences near Barcelona, Spain, told The Associated Press.
It's traveling at a speed of about 152,000 mph and approaching the inner solar system from the bar of the Milky Way, Live Science reported. Its trajectory suggests it did not originate in this solar system, according to EarthSky.org.

This is only the third time in history that an interstellar object entering the inner solar system has been recorded.
A cigar-shaped interstellar object called "Oumuamua," the Hawaiian word for "scout," was detected in 2017. And in 2019, an object named "21/Borisov" -- a comet that likely strayed from another star system -- was located.
Astronomers will continue to investigate the size and physical properties of the comet through September, after which it will pass too close to the sun to remain visible, NASA said.
The comet is expected to reappear on the other side of the sun in early December, NASA said.
Quelle: abcNews
+++
ESA tracks rare interstellar comet
Astronomers have confirmed the discovery of a rare celestial visitor: a comet from beyond our Solar System.
Officially named 3I/ATLAS, this newly identified interstellar object is only the third of its kind ever observed, following the famous 1I/ʻOumuamua in 2017 and 2I/Borisov in 2019.
A visitor from beyond the void
The comet was first spotted on 1 July 2025 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) telescope in Río Hurtado, Chile. Its unusual trajectory immediately raised suspicions that it originated from interstellar space. This was later confirmed by astronomers around the world, and the object was given its formal designation: 3I/ATLAS, indicating its status as the third known interstellar object.
3I/ATLAS is approximately 670 million kilometres from the Sun and will make its closest approach in late October 2025, passing just inside the orbit of Mars. It is thought to be up to 20 kilometres wide and is travelling roughly 60 km/s relative to the Sun. It poses no danger to Earth, coming no closer than 240 million kilometres – over 1.5 times the distance between Earth and the Sun.
ESA tracks the interstellar interloper
ESA's Planetary Defence Office responded promptly to the discovery. Automated detection systems alerted ESA’s astronomers, who are contributing to global efforts to track the comet’s path and to find evidence of its existence in older data – a process known as ‘precovery.’

ESA astronomers are using telescopes in Hawaii, Chile, and Australia to monitor the comet’s progress. Some of these telescopes are owned by ESA, others are provided as part of longstanding partnerships.
These efforts are part of ESA’s broader mission to detect, track, and characterise near-Earth objects – though 3I/ATLAS is not considered one, due to its distance from our planet.
Scientists will now be interested in learning more about this interstellar visitor’s composition and behaviour.
3I/ATLAS is an active comet. If it heats up sufficiently as it nears our star, it could begin to sublimate – a process in which frozen gases transform directly into vapour, carrying dust and ice particles into space to form a glowing coma and tail.
However, by the time the comet reaches its closest point to Earth, it will be hidden behind the Sun. It is expected to reappear by early December, offering astronomers another window for study.
A remnant from a distant world
What makes interstellar objects like 3I/ATLAS so extraordinary is their absolutely foreign nature. While every planet, moon, asteroid, comet and lifeform that formed in our Solar System shares a common origin, a common heritage, interstellar visitors are true outsiders. They are remnants of other planetary systems, carrying with them clues about the formation of worlds far beyond our own.
It may be thousands of years until humans visit a planet in another solar system and interstellar comets offer the tantalising opportunity for us to touch something truly otherworldly.
These icy wanderers offer a rare, tangible connection to the broader galaxy – to materials formed in environments entirely unlike our own. To visit one would be to connect humankind with the Universe on a far greater scale.
ESA mission will intercept the unknown

To this end, ESA is preparing the Comet Interceptor mission. The spacecraft will be launched in 2029 into a parking orbit at the Sun–Earth Lagrange Point 2 (L2), lying in wait for a suitable target – a pristine comet from the distant Oort Cloud that surrounds our Solar System, or, unlikely but highly appealing, an interstellar object.
While it is improbable that we will discover an interstellar object that is reachable for Comet Interceptor, as a first demonstration of a rapid response mission that waits in space for its target, it will be a pathfinder for possible future missions to intercept these mysterious visitors.
Whether it’s 1I/‘Oumuamua, 2I/Borisov, 3I/ATLAS or the future target of an interceptor mission, each new interstellar visitor reminds us that we are part of a vast and dynamic galaxy – and that sometimes, the Universe comes to us.
Quelle: ESA
