.

STS-8
Space Shuttle: Challenger
Launch Pad: 39A
Launch Weight: 242,742 pounds
Launched: Aug. 30, 1983 at 2:32:00 a.m. EDT
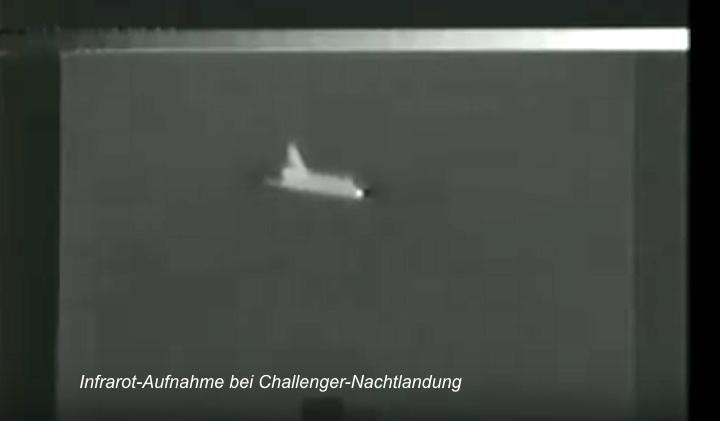
Landing Site: Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.
Landing: Sept. 5, 1983 at 12:40:43 a.m. PDT
Landing Weight: 203,945 pounds
Runway: 22
Rollout Distance: 9,371 feet
Rollout Time: 50 seconds
Revolution: 98
Mission Duration: 6 days, 1 hour, 8 minutes and 43 seconds
Returned to KSC: Sept. 9, 1983
Orbit Altitude: 191 nautical miles
Orbit Inclination: 28.5 degrees
Miles Traveled: 2.5 million
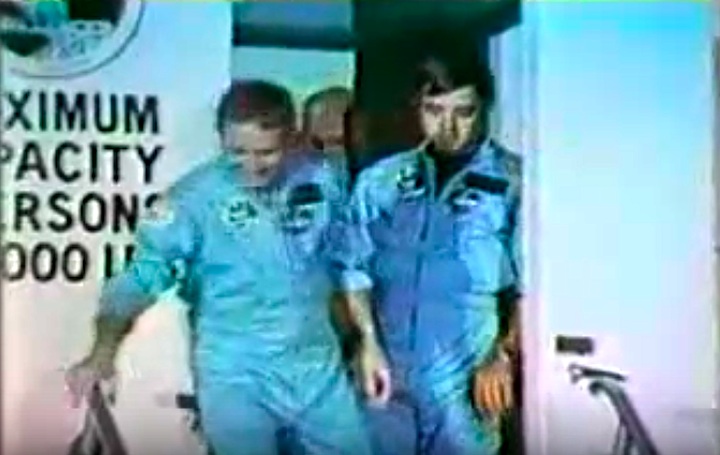
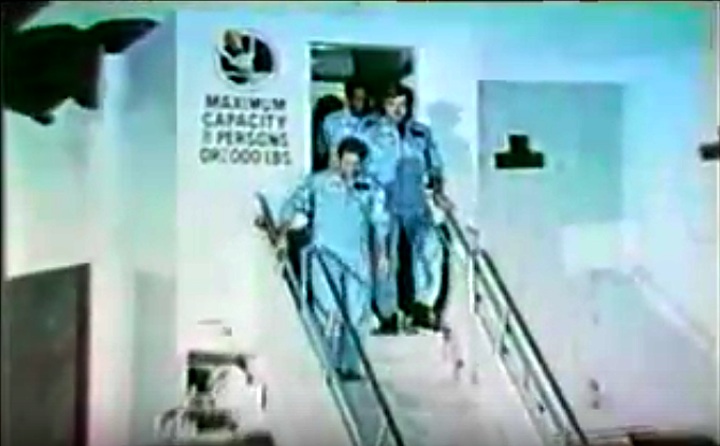
Crew Members

Image above: STS-8 Crew photo with Commander Richard H. Truly, Pilot Daniel C. Brandenstein and Mission Specialists Dale A. Gardner, Guion S. Bluford, Jr. and William E. Thornton. Image Credit: NASA
Mission Highlights
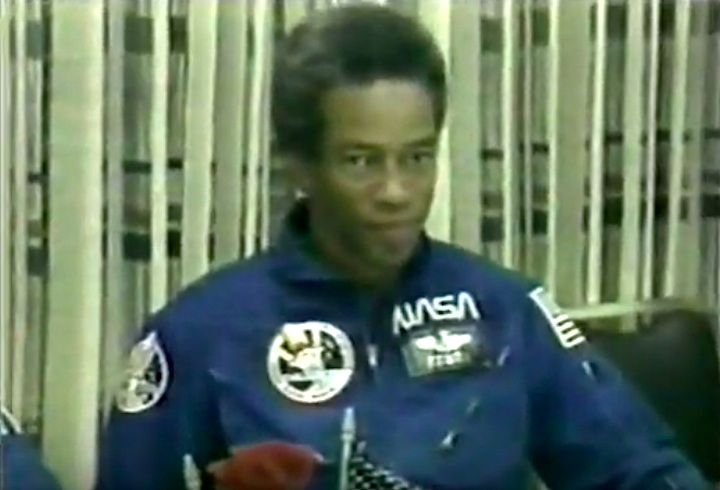
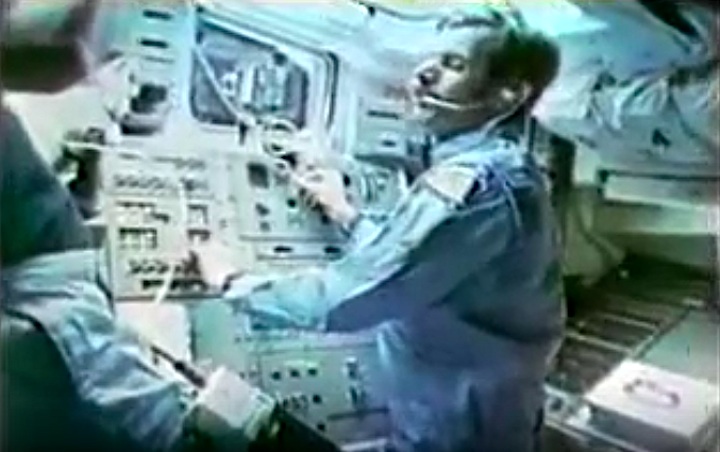
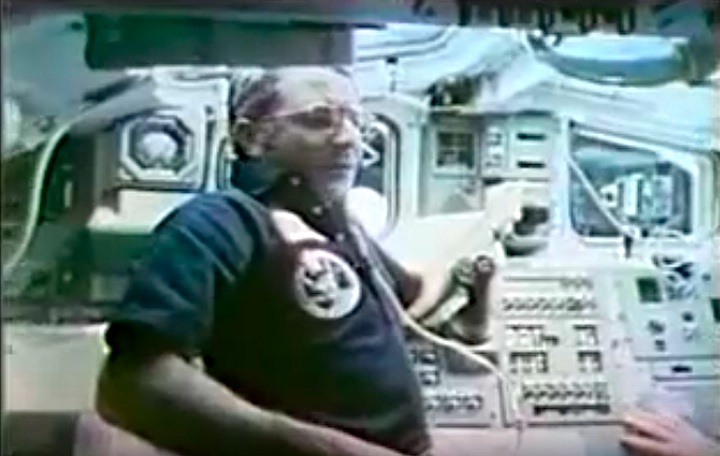
 Bluford became the first African-American to fly in space. INSAT-1B, a multipurpose satellite for India which was attached to the Payload Assist Module-D (PAM-D) motor, was deployed. The nose of orbiter was held away from the sun for 14 hours to test the flight deck area in extreme cold. For the Development Flight Instrumentation Pallet (DFI PLT), the crew filmed performance of an experimental heat pipe mounted in the cargo bay; also, the orbiter dropped to 139 miles altitude to perform tests on thin atomic oxygen to identify the cause of glow that surrounds parts of the orbiter at night. The remote manipulator system was tested to evaluate joint reactions to higher loads. The following biofeedback experiment was conducted: six rats were flown in the Animal Enclosure Module to observe animal reactions in space. Other payloads on this mission: Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES); Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSlP) experiment; Incubator-Cell Attachment Test (l CAT); Investigation of STS Atmospheric Luminosities (ISAL); Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME); and five Get Away Special experiment packages including eight cans of postal covers. Testing was conducted between the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-I (TDRS-1) and the orbiter using a Ku-band antenna, and investigations continued on the Space Adaptation Syndrome.
Bluford became the first African-American to fly in space. INSAT-1B, a multipurpose satellite for India which was attached to the Payload Assist Module-D (PAM-D) motor, was deployed. The nose of orbiter was held away from the sun for 14 hours to test the flight deck area in extreme cold. For the Development Flight Instrumentation Pallet (DFI PLT), the crew filmed performance of an experimental heat pipe mounted in the cargo bay; also, the orbiter dropped to 139 miles altitude to perform tests on thin atomic oxygen to identify the cause of glow that surrounds parts of the orbiter at night. The remote manipulator system was tested to evaluate joint reactions to higher loads. The following biofeedback experiment was conducted: six rats were flown in the Animal Enclosure Module to observe animal reactions in space. Other payloads on this mission: Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES); Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSlP) experiment; Incubator-Cell Attachment Test (l CAT); Investigation of STS Atmospheric Luminosities (ISAL); Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME); and five Get Away Special experiment packages including eight cans of postal covers. Testing was conducted between the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-I (TDRS-1) and the orbiter using a Ku-band antenna, and investigations continued on the Space Adaptation Syndrome.---
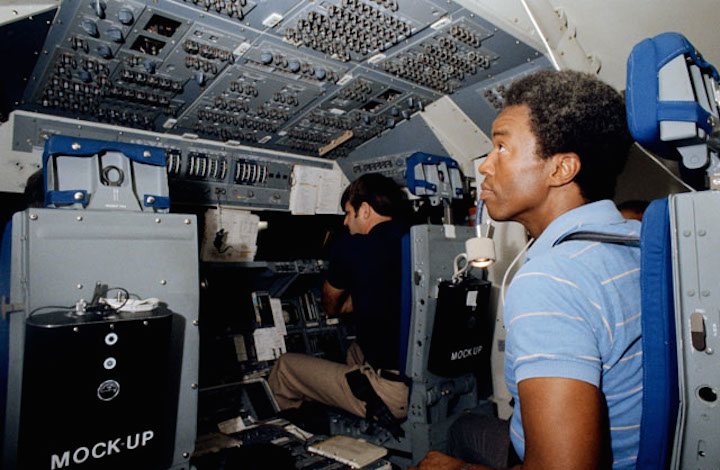

S83-33032 (23 May 1983) --- Astronauts Guion S. Bluford, right, and Daniel C. Brandenstein man their respective Challenger entry and ascent stations in the Shuttle Mission Simulator (SMS) at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC) during a training session for the STS-8 mission. Brandenstein is in the pilot's station, while Bluford, a mission specialist, occupies one of the two aft flight deck seats. Both are wearing civilian clothes for this training exercise. This motion based simulator represents the scene of a great deal of training and simulation activity, leading up to crew preparedness for Space Transportation System (STS) mission. Photo credt: NASA/Otis Imboden, National Geographic
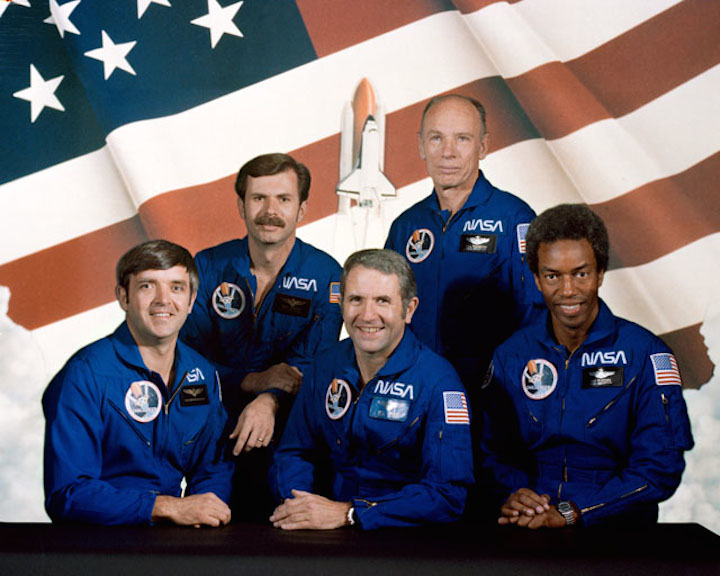

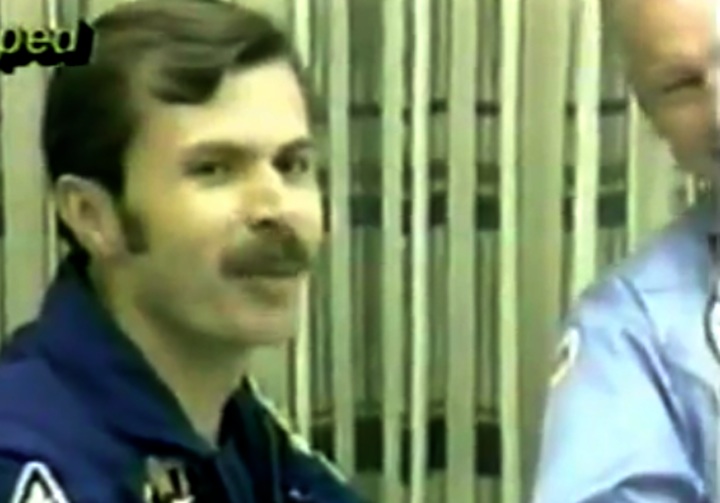
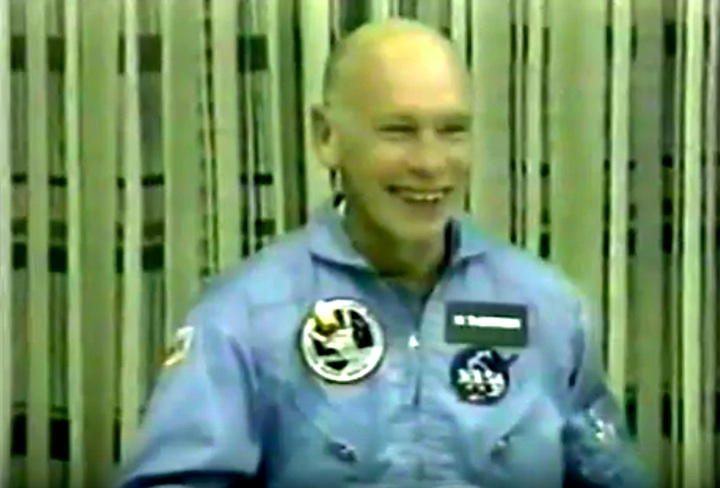
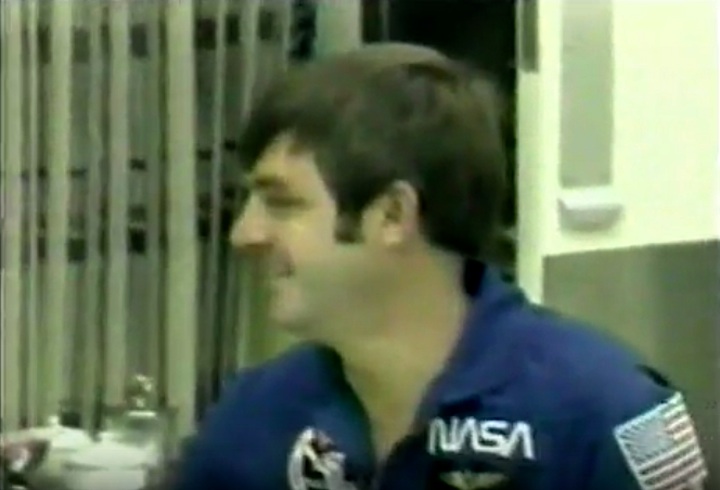
S83-31724 (29 April 1983) --- These five astronauts will be the crew members for STS-8 in the space shuttle Challenger in later summer of this year. Richard M. Truly, center, is the crew commander. Daniel C. Brandenstein, left, is pilot. The mission specialists are Dale A. Gardner, William E. Thornton (both on back row) and Guion S. Bluford. The backdrop is a Challenger launch and the American flag. Photo credit: NASA
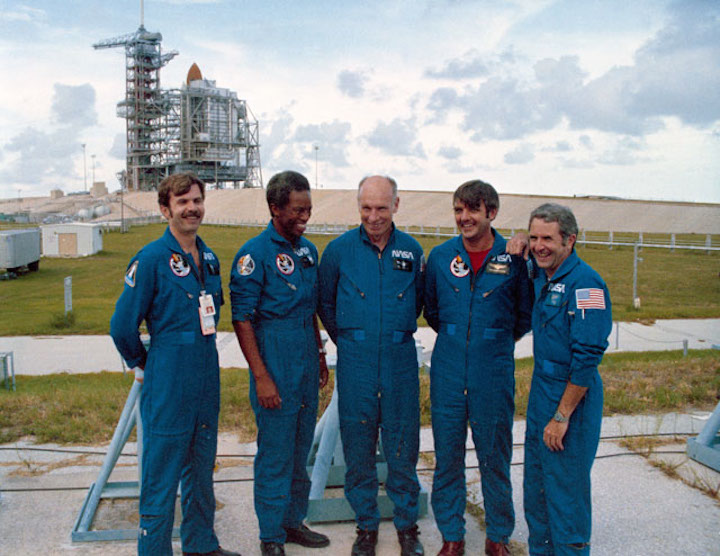

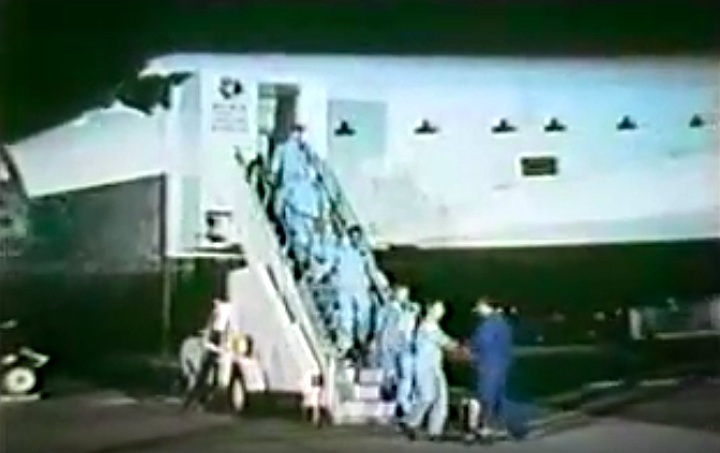
S83-38389 (6 Aug. 1983) --- The STS-8 crew members pause for a crew photo at Pad 39A after a question and answer session with the press. They were about to participate in the STS-8 countdown demonstration test. They will repeat many of their measures on Aug. 30 when they are scheduled to lift off aboard the space shuttle Challenger. From left to right are astronauts Dale A. Gardner, Guion S. Bluford, Dr. William E. Thornton, all mission specialists; Daniel C. Brandenstein, pilot; and Richard F. Truly, commander. The Challenger is in the background at complex 39.
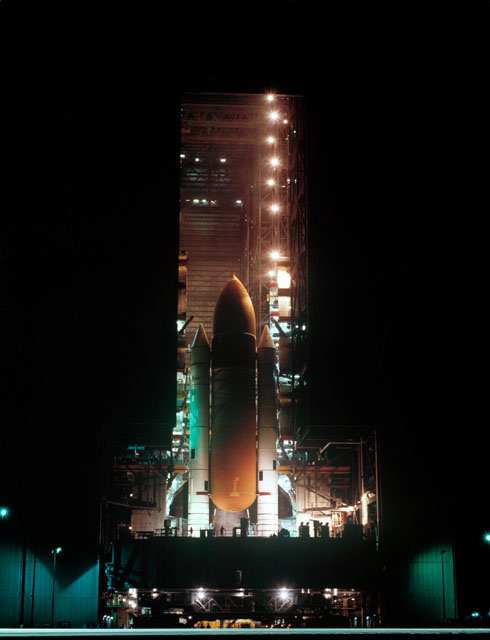

S83-39238 (1 Aug. 1983) --- The giant cluster of spaceflight hardware for NASA's eighth Space Transportation System (STS) mission begins its slow move to the launch pad at launch complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Following its mating to the two solid rocket boosters (SRB) and the external fuel tank (ET) in the huge vehicle assembly building (VAB), the space shuttle Challenger is slowly moved to the launch pad atop the mobile launch platform. Photo credit: NASA
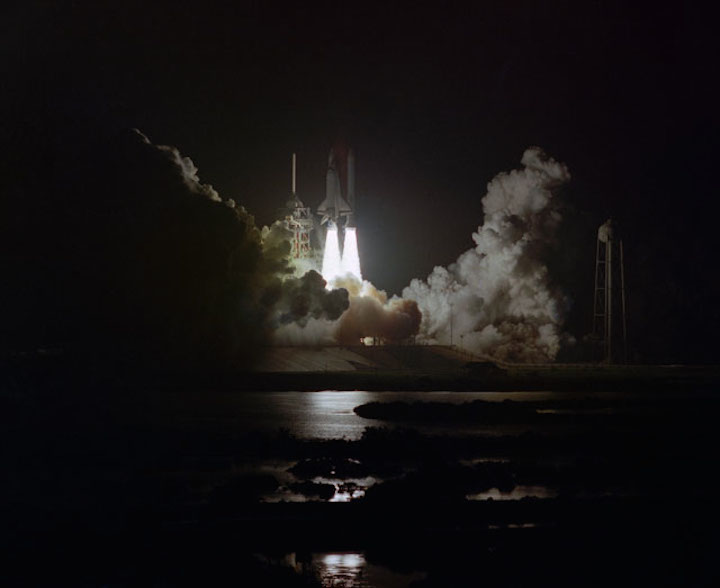

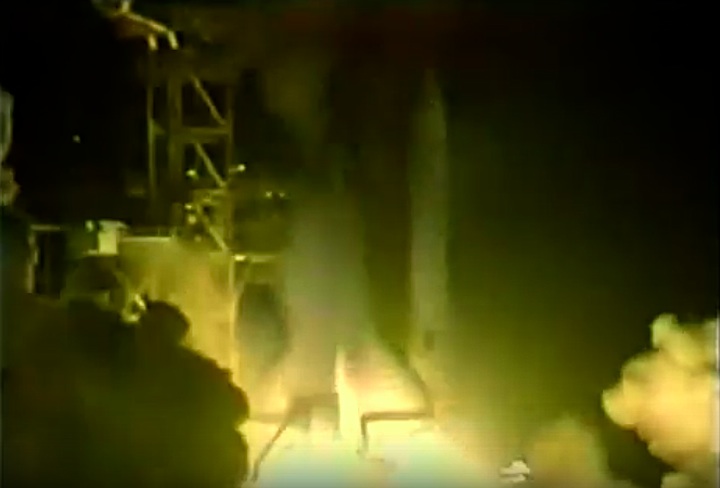
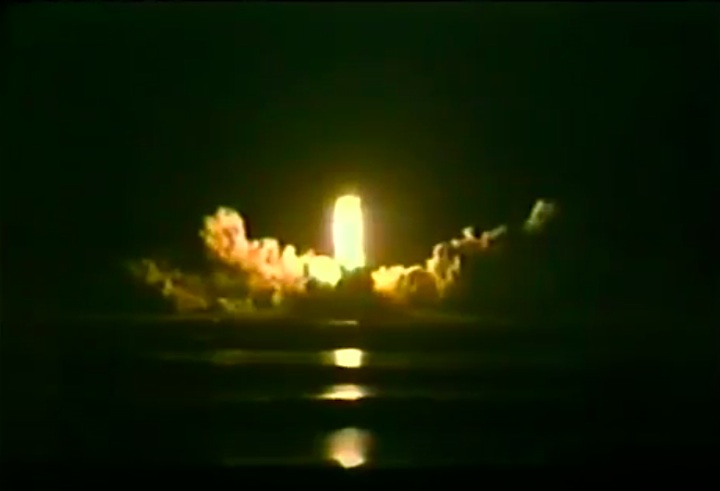
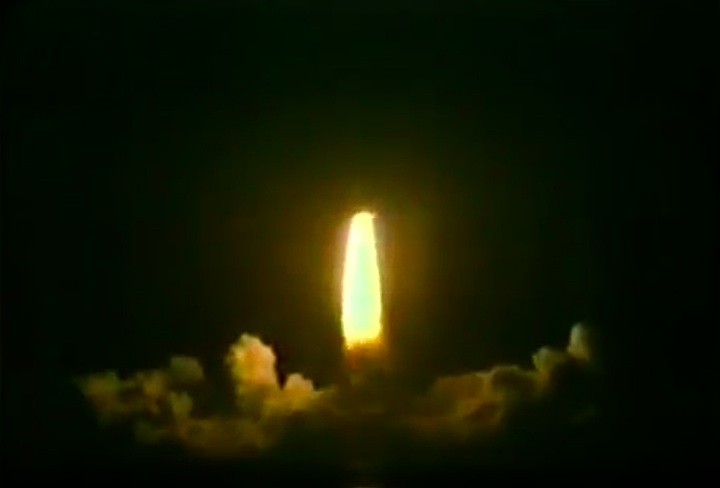
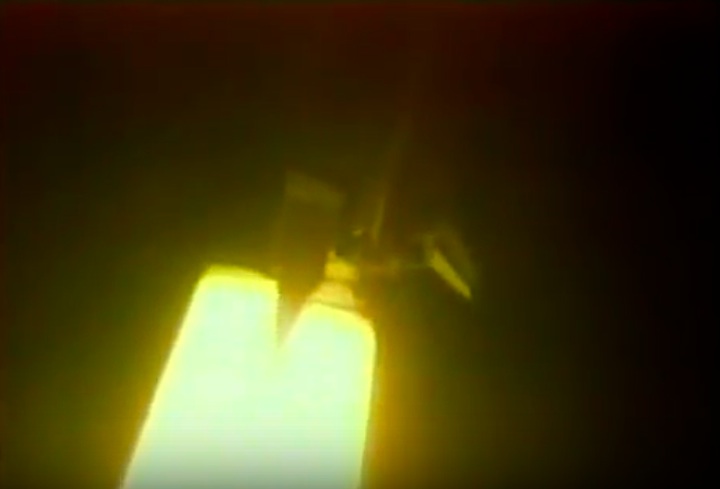
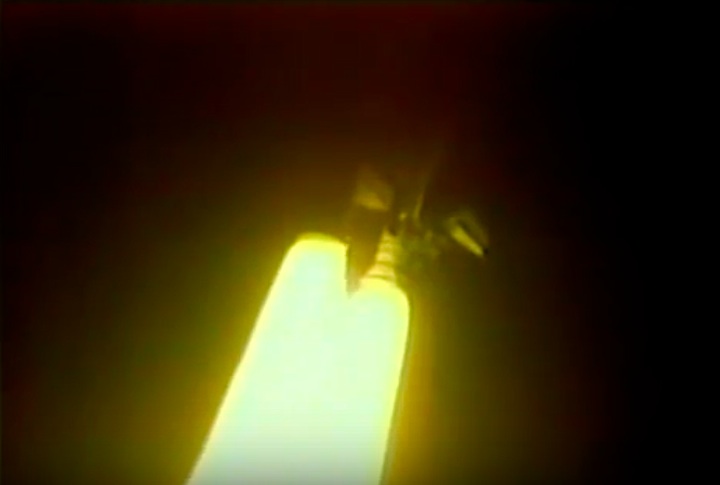
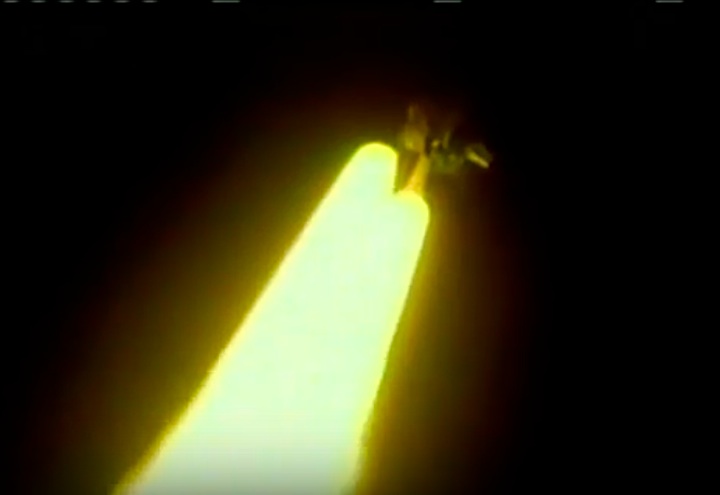
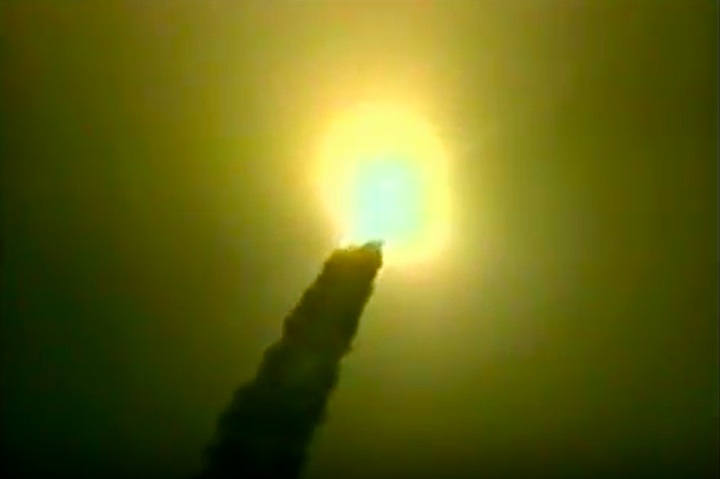
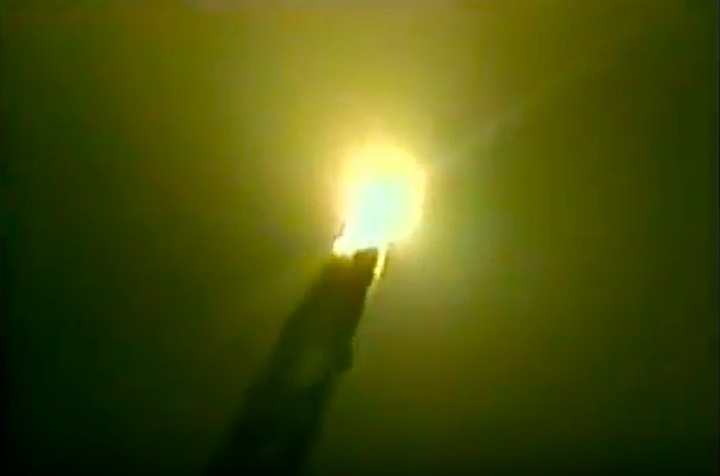
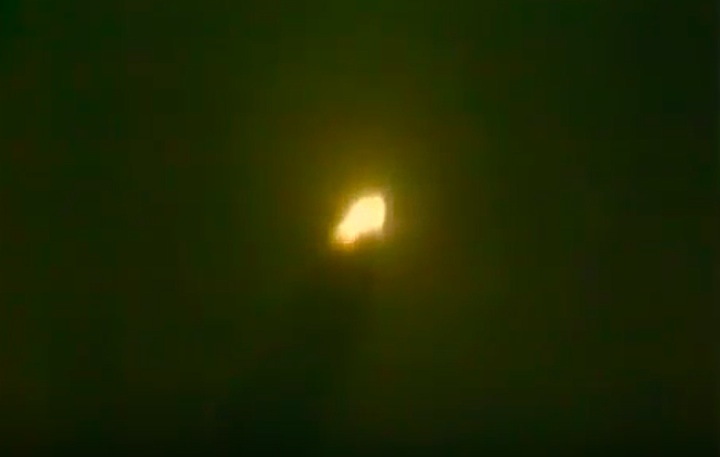
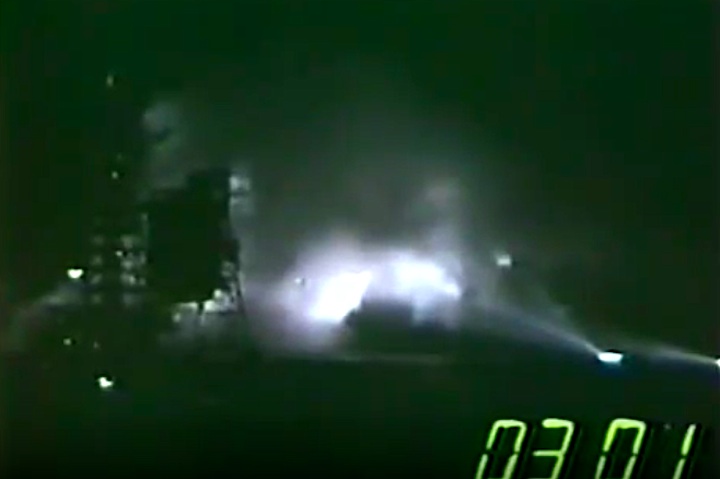
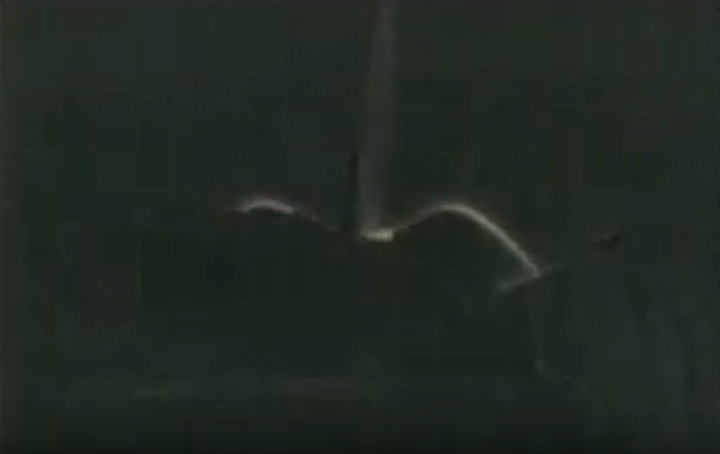
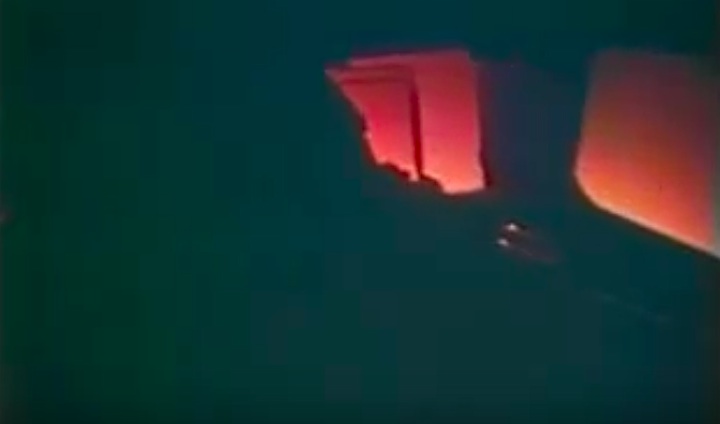
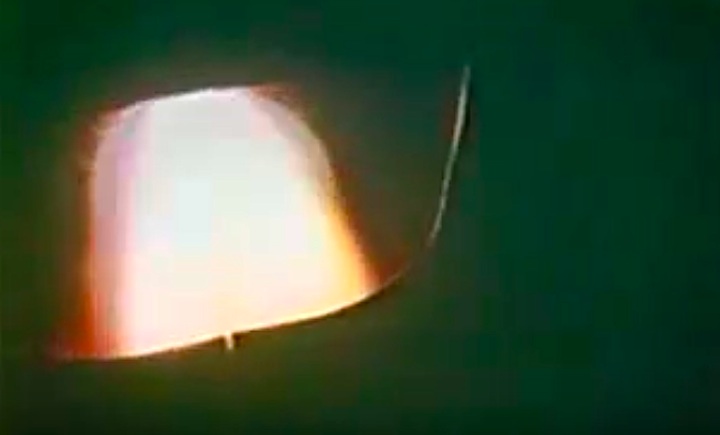
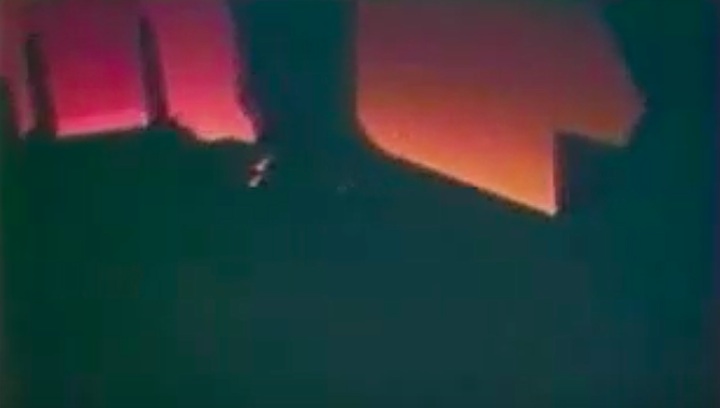
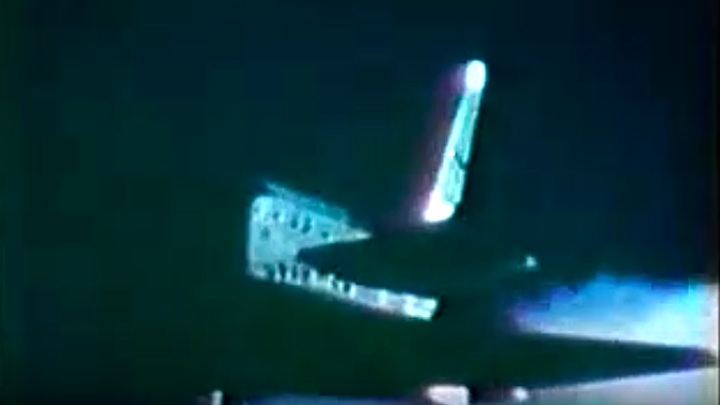
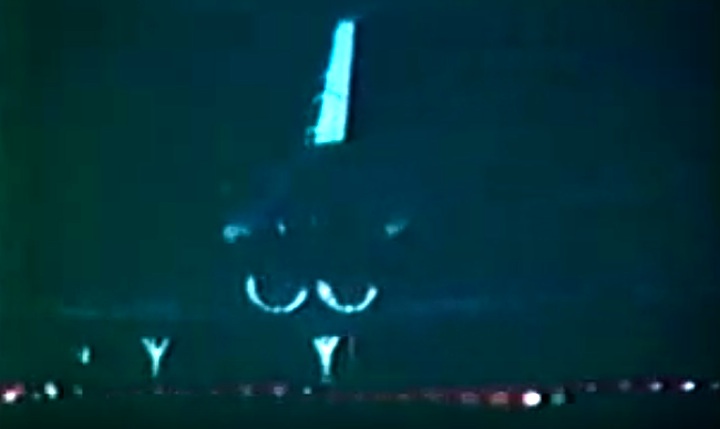
S83-39512 (30 Aug. 1983) --- NASA's eighth space shuttle launch lights up the Florida sky at 2:32 a.m. (EDT), Aug. 30, 1983. The space shuttle Challenger's third flight is the first to have its beginnings in darkness. Five astronauts and an assortment of experiments are aboard the reusable vehicle. Crew members are astronauts Richard H. Truly, STS-8 commander; Daniel C. Brandenstein, pilot; and Dale A. Gardner, Guion S. Bluford and William E. Thornton, all mission specialists. Photo credit: NASA
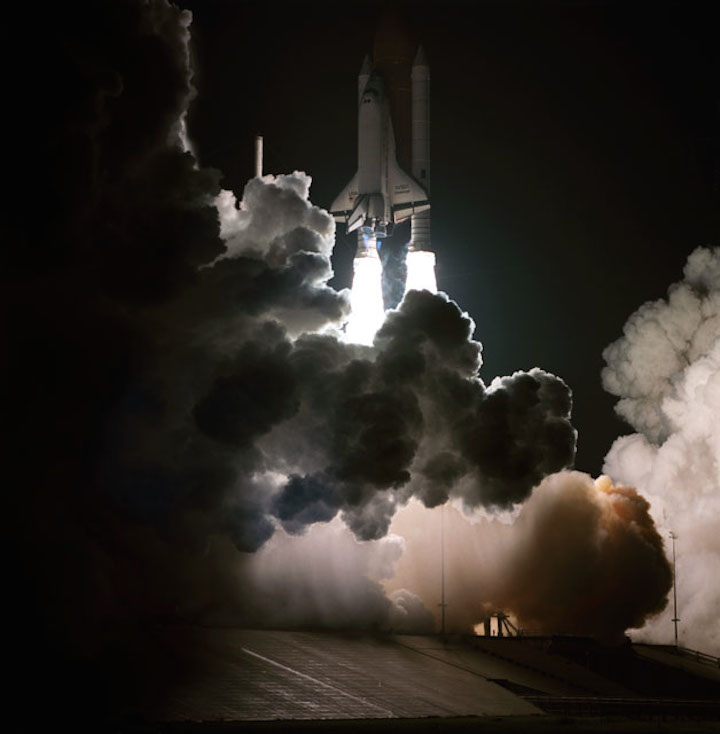

S83-39513 (30 Aug. 1983) --- NASA's eighth space shuttle launch lights up the Florida sky at 2:32 a.m. (EDT), Aug. 30, 1983. The Challenger's third flight is the first to have its beginnings in darkness. Five astronauts and an assortment of experiments are aboard the reusable vehicle. Crew members are astronauts Richard H. Truly, STS-8 commander; Daniel C. Brandenstein, pilot; and Dale A. Gardner, Guion S. Bluford and William E. Thornton, all mission specialists. Photo credit: NASA
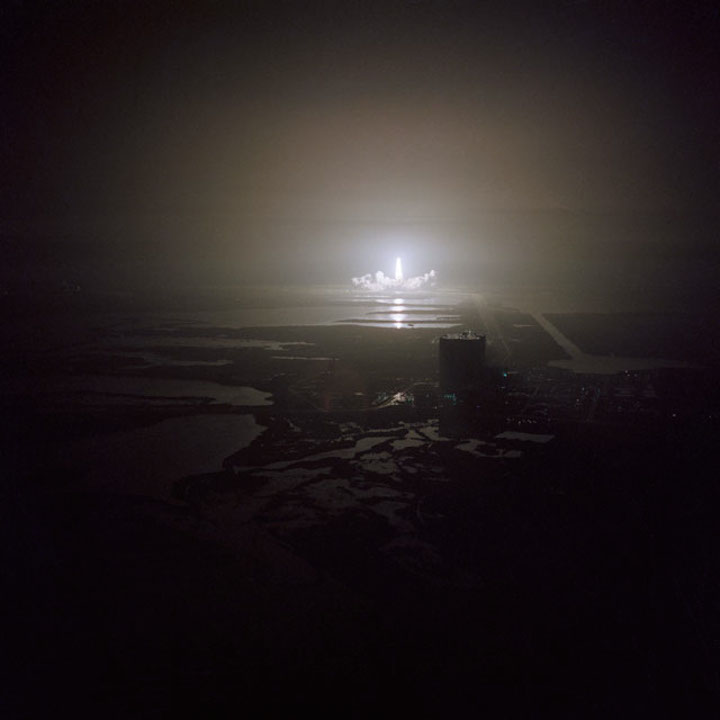

S83-39567 (30 Aug. 1983) --- The nighttime liftoff of the space shuttle Challenger casts a brilliant glow across the marshy Kennedy Space Center (KSC) landscape. This aerial view from west of the vehicle assembly building (VAB) shows the Challenger climbing toward space just after its 2:32 a.m. (EDT) launch to begin the STS-8 mission. Photo credit: NASA
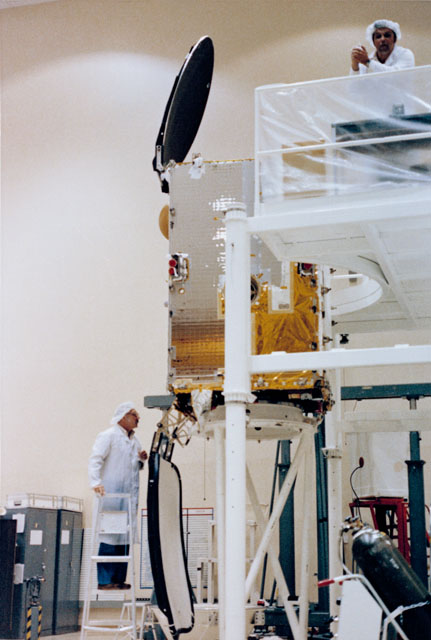

S83-36307 (2 June 1983) --- INSAT 1-B is being prepared for its trip aboard the space shuttle Challenger and its deployment for geosynchronous orbital duties at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and at NASA's Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The Indian National Satellite is the second such Indian communications/meteorological spacecraft, the first having been sent into space via a Delta launch vehicle. The STS-8 astronaut crew members and a payload assist module (PAM) will aid the newest INSAT in its deployment steps during NASA's third Challenger flight in August of this year.
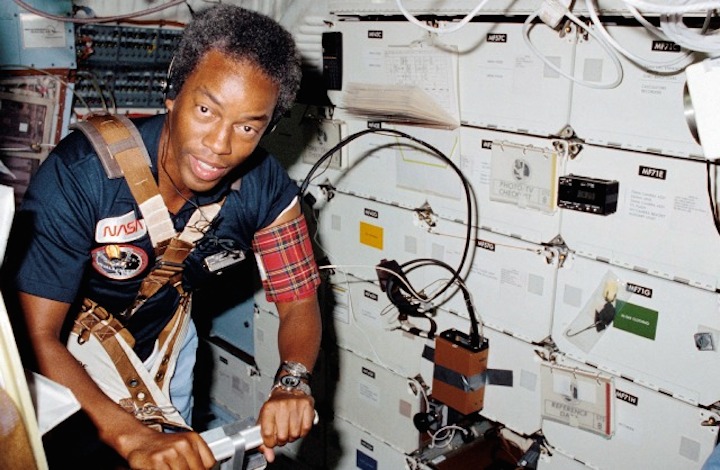

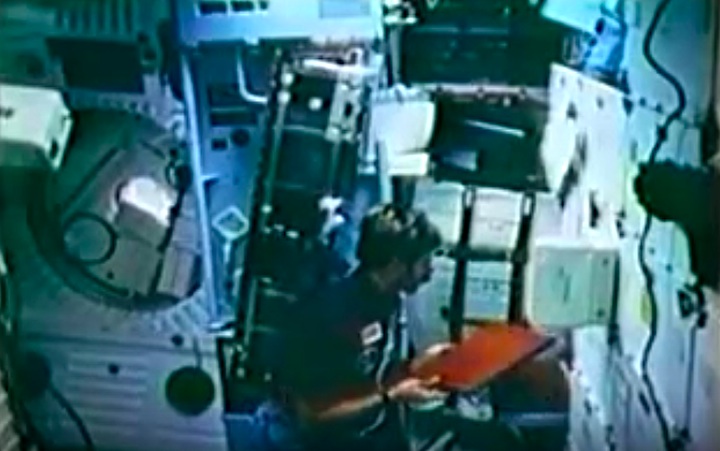
STS008-13-0361 (30 Aug.-5 Sept. 1983) --- Astronaut Guion S. Bluford, STS-8 mission specialist, assists Dr. William E. Thornton (out of frame) with a medical test that requires use of the treadmill exercising device designed for spaceflight by the STS-8 medical doctor. This frame was shot with a 35mm camera. Photo credit: NASA
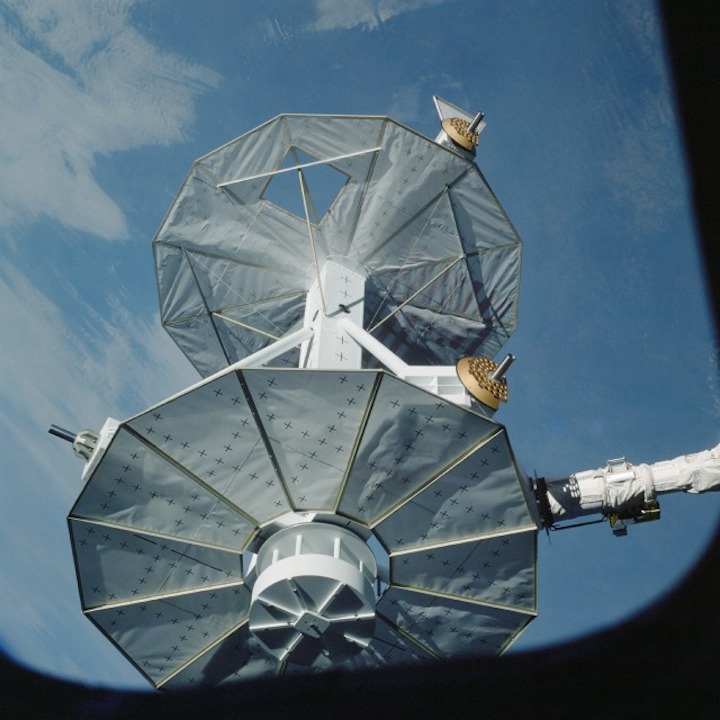

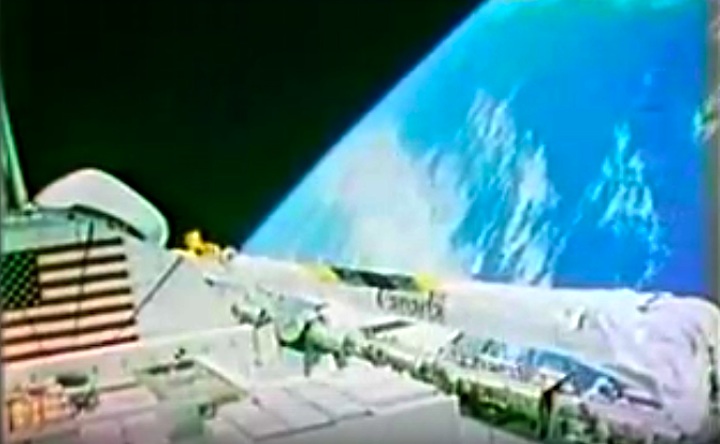
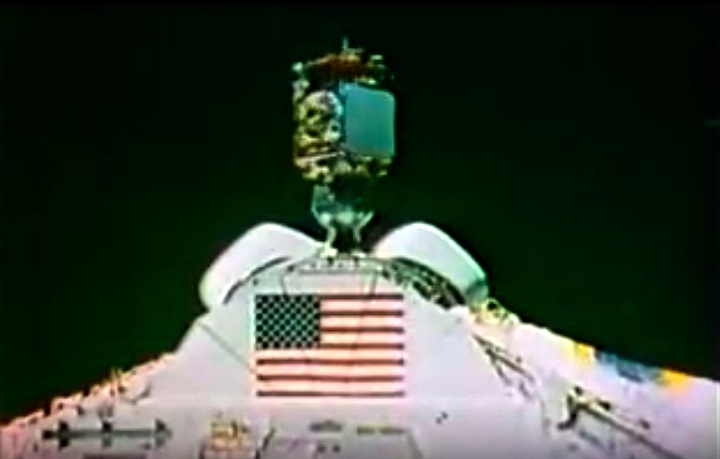
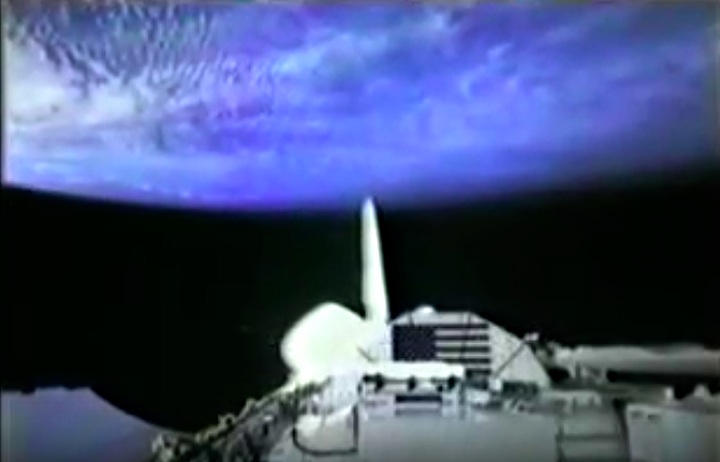
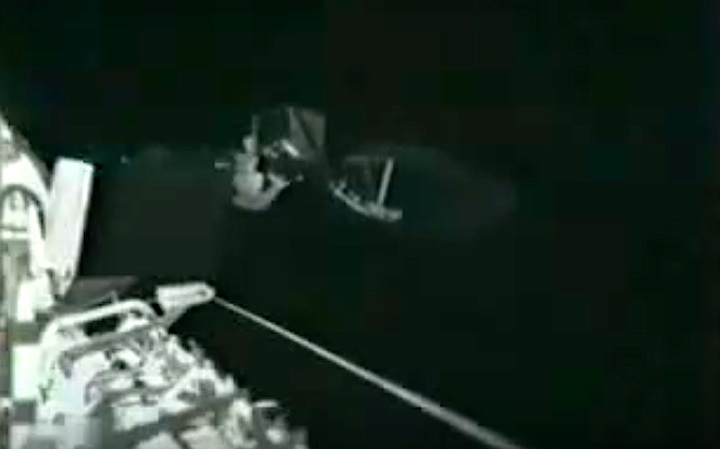
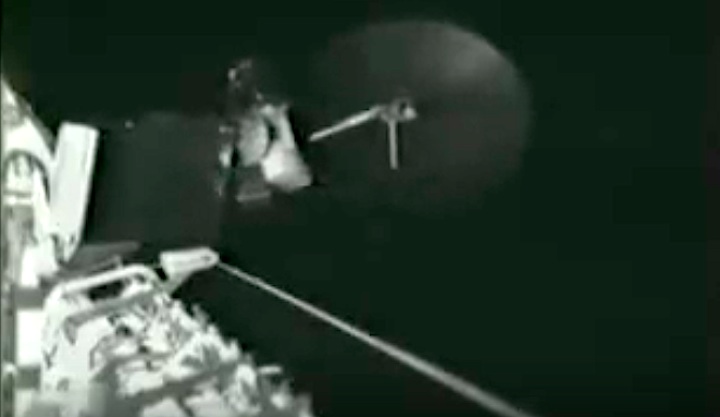
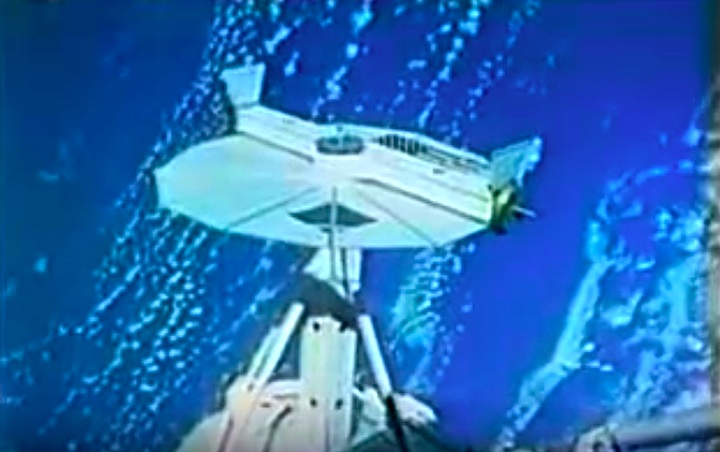
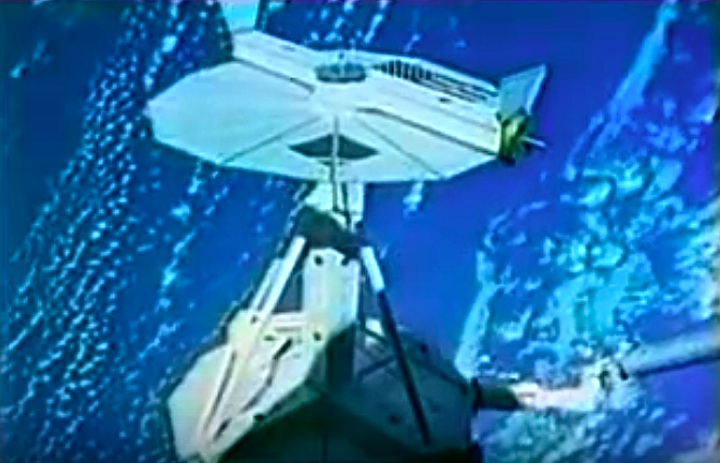
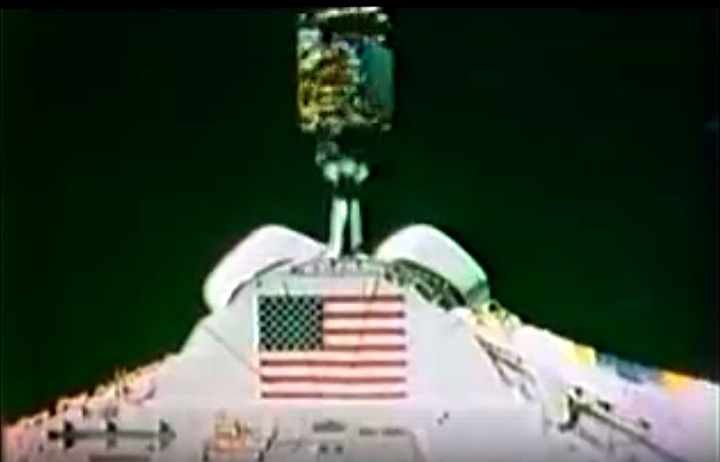
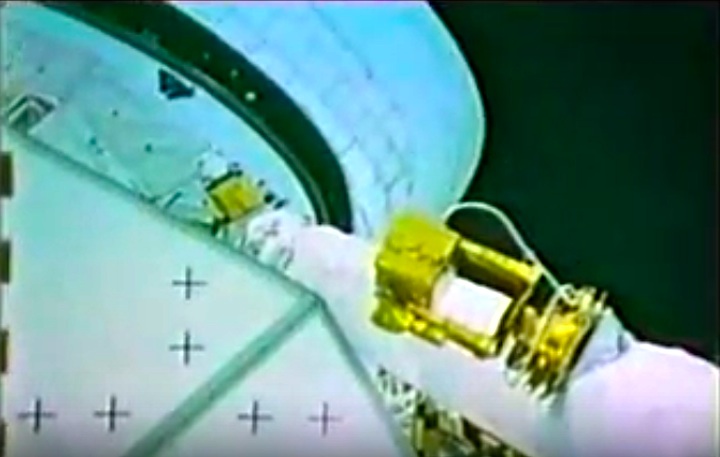
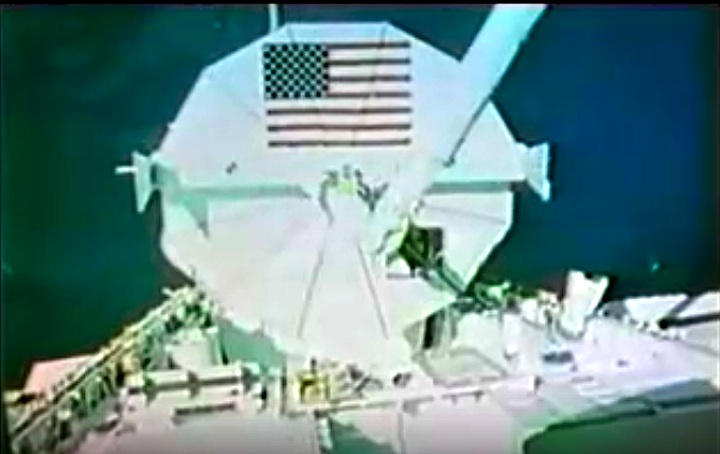
STS008-35-1239 (30 Aug.-5 Sept. 1983) --- The space shuttle Challenger's payload flight test article (PFTA) is lifted from the cargo bay and held over clouds and water on Earth. The 70mm frame was photographed by one of the five STS-8 crew members with a free hand during the busy RMS/PFTA agenda. Photo credit: NASA
---
Frams von STS-8 Challenger Mission NASA-Video:
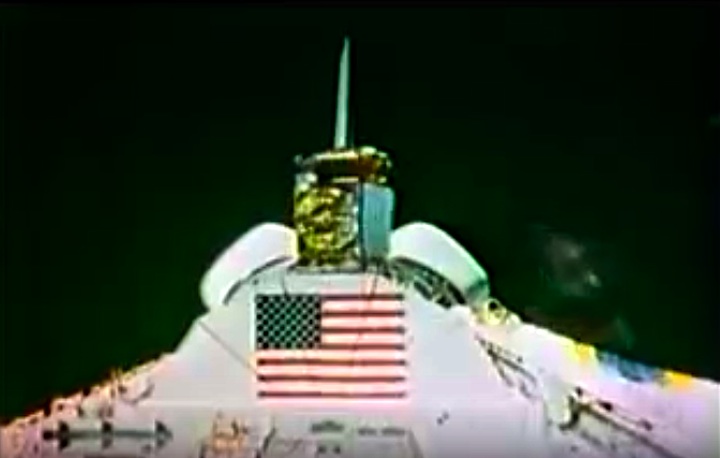
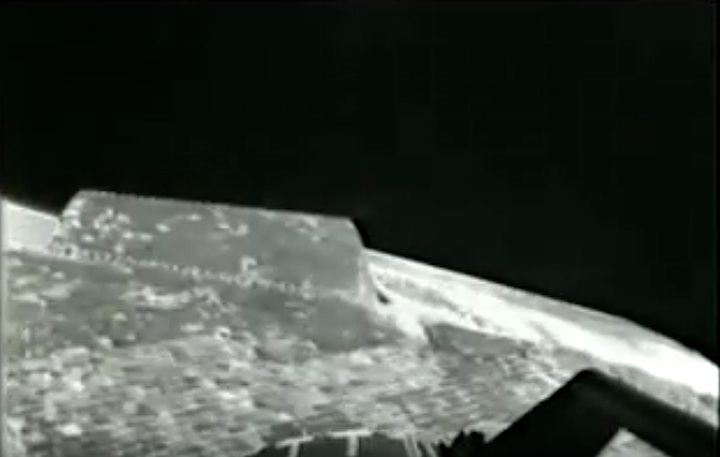
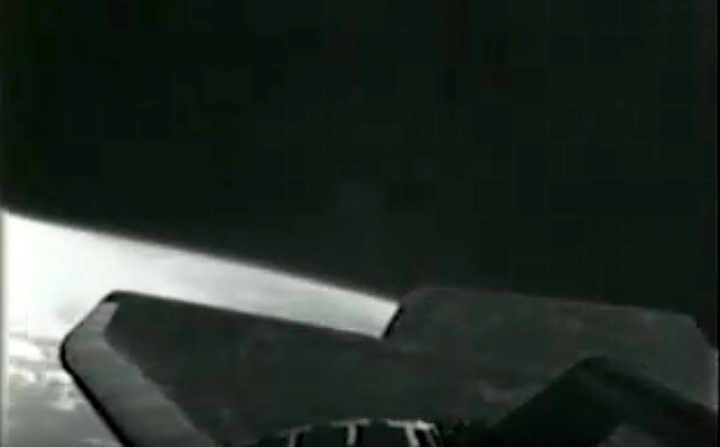











































































Quelle: NASA
4397 Views
