.
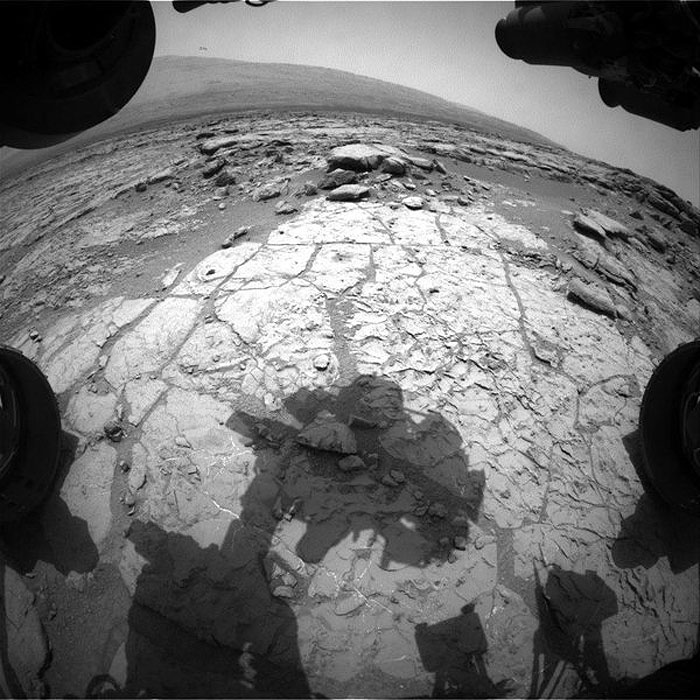

A Martian view from one of Curiosity's hazard avoidance cameras, transmitted back to Earth on Thursday, shows the shadow of the instrument turret on the rover's robotic arm.
.
NASA's Curiosity rover is back in business after a weeks-long communication gap caused by solar interference. The proof comes in the form of pictures transmitted back to Earth on Thursday from the 1-ton machine's vantage point at Yellowknife Bay on Mars.
NASA's Red Planet probes were on hiatus for most of April due to an unfavorable alignment of Mars, Earth and the sun. During solar conjunction, the sun gets in the way of the communication lines between the two planets, and mission controllers generally put science operations on hold. Such conjunctions occur every 26 months. Opportunity has gone through several communication breaks during its nine years on Mars, but this is the first one to occur since Curiosity landed last August.
The spacecraft weren't completely idle during the break: Curiosity conducted in-place investigations and sent back limited transmissions via X-band radio to let controllers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory know that it was doing OK. Opportunity autonomously flipped its computer into safe mode during the break, apparently due to a glitch involving a routine camera check. A fresh set of software commands fixed the glitch, and on Wednesday controllers reported that Opportunity was back in working order.
Curiosity is due for its own software upgrade, and then the rover is scheduled to drill out a second sample of ground-up rock for analysis. The first sample, analyzed in March, suggested that the Yellowknife Bay environment was potentially habitable billions of years ago. Scientists want to use the follow-up sample to confirm what they saw in previous chemical analyses.
After Curiosity finishes up its work in Yellowknife Bay and its surroundings in the Glenelg area of Gale Crater, controllers plan to point the rover toward Mount Sharp, 6 miles (10 kilometers) away. The science team suspects that the mountain's many layers of rock will hold further evidence of ancient organic chemistry.
.
ChemCam: Remote Micro-Imager
2013-05-02 06:52:50 UTC
.
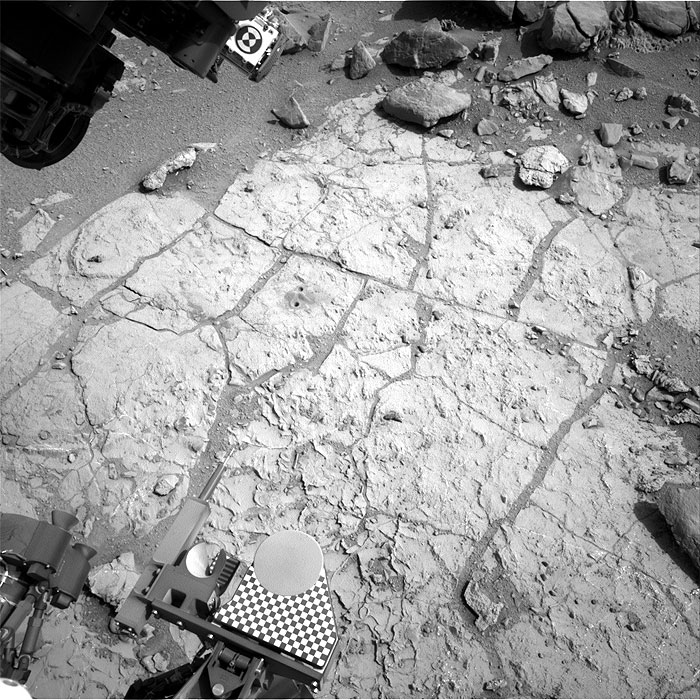

This image was taken by Navcam: Right B (NAV_RIGHT_B) onboard NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 262 (2013-05-02 09:47:53 UTC).
.
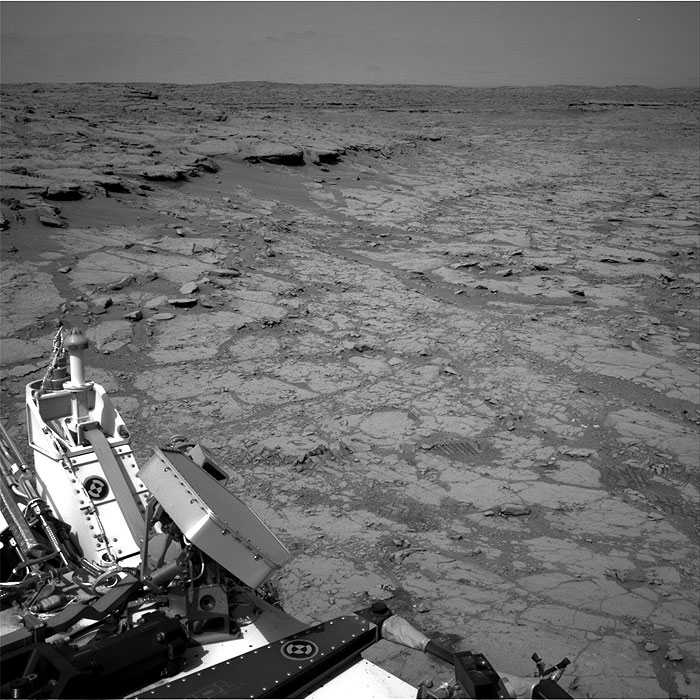

This image was taken by Navcam: Right B (NAV_RIGHT_B) onboard NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 262 (2013-05-02 09:50:08 UTC).
.
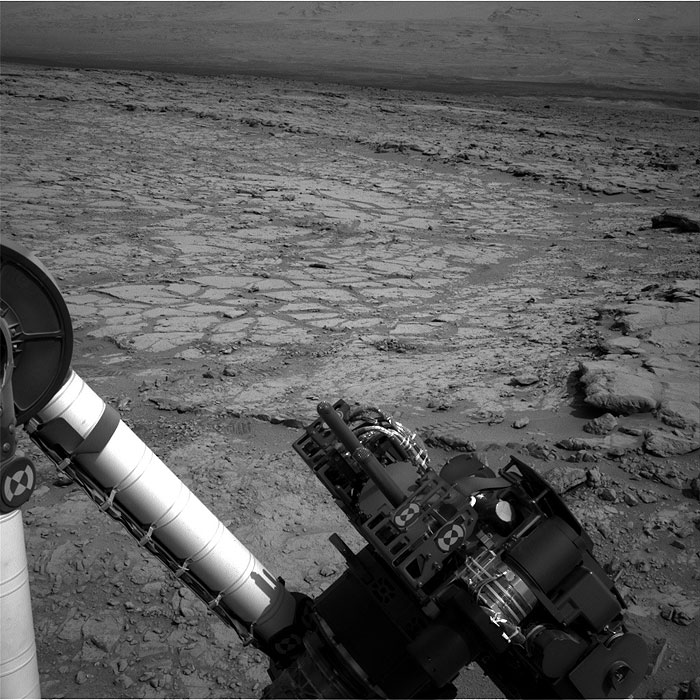

This image was taken by Navcam: Right B (NAV_RIGHT_B) onboard NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 262 (2013-05-02 09:51:52 UTC).
.
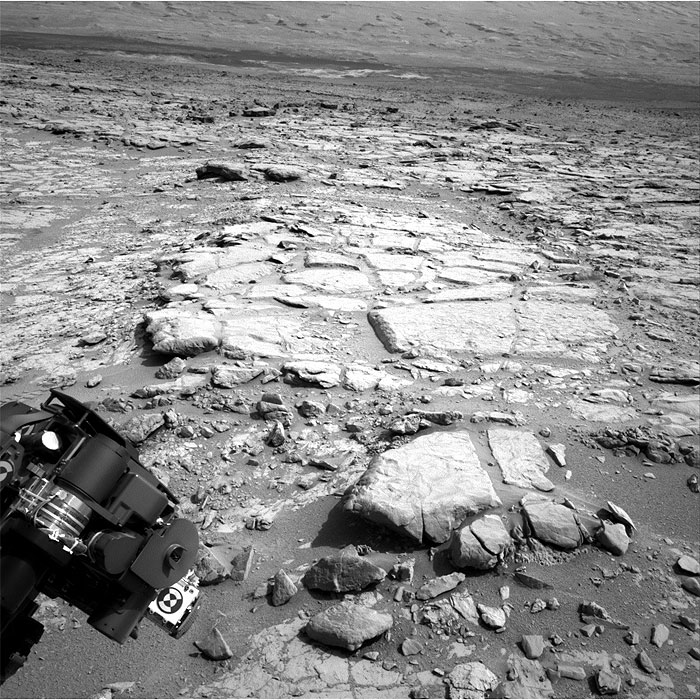

This image was taken by Navcam: Right B (NAV_RIGHT_B) onboard NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 262 (2013-05-02 09:52:27 UTC).
.
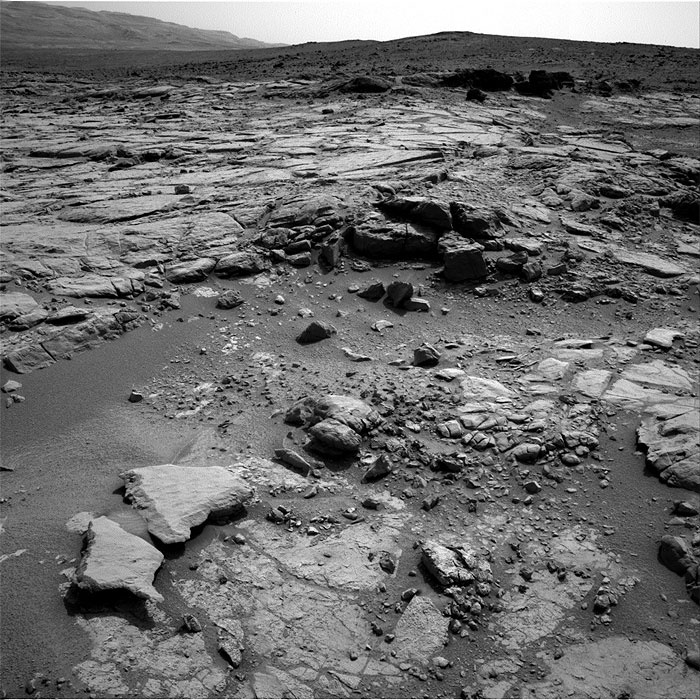

This image was taken by Navcam: Right B (NAV_RIGHT_B) onboard NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 262 (2013-05-02 09:53:37 UTC).
.
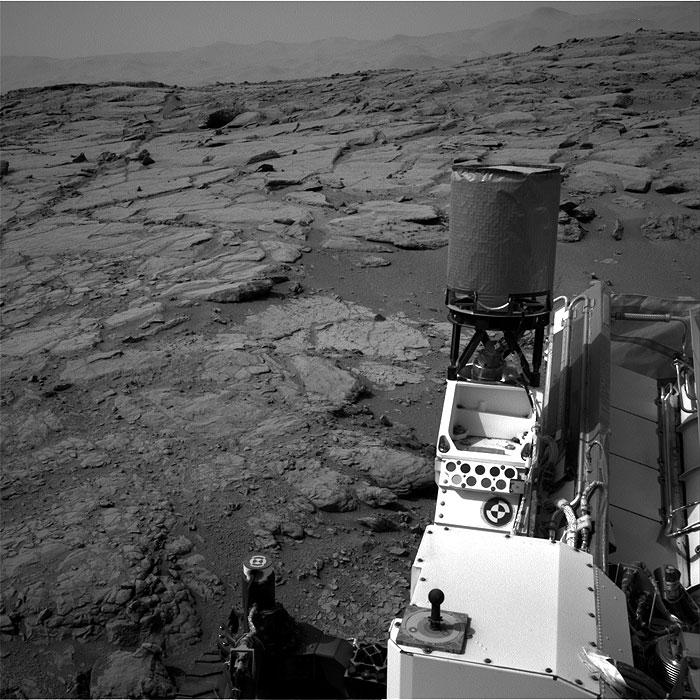

This image was taken by Navcam: Right B (NAV_RIGHT_B) onboard NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 262 (2013-05-02 09:55:50 UTC).
.
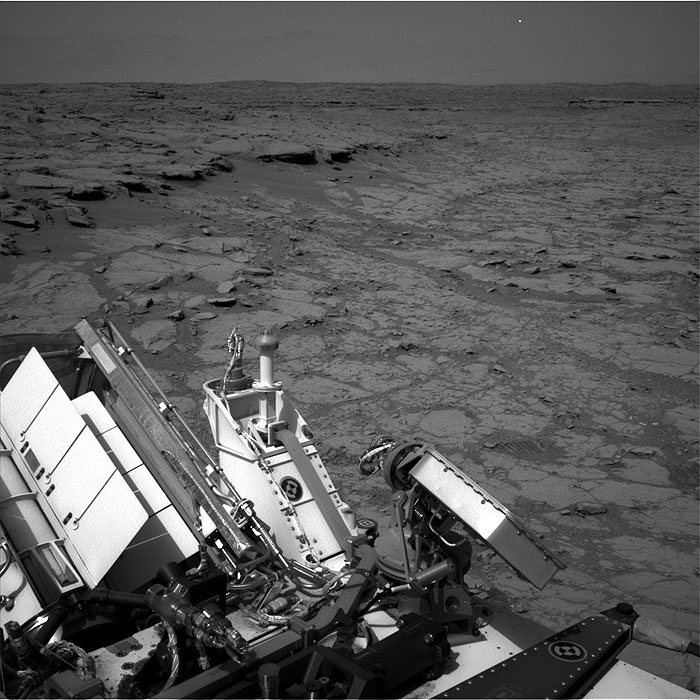

This image was taken by Navcam: Left B (NAV_LEFT_B) onboard NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 262 (2013-05-02 09:50:08 UTC).
.
4942 Views

